Decentralization in blockchain is revolutionizing the way digital systems are built and maintained. By shifting control away from central authorities, this innovative approach fosters enhanced security, resilience, and transparency across various industries.
This article explores the multifaceted dimensions of decentralization in blockchain, providing a detailed look at its technical, political, and logical components, as well as the benefits and real-world applications driving today’s digital transformation.
Understanding The Concept
Decentralization in blockchain is not merely a technical attribute—it is a transformative philosophy underpinning distributed systems’ operation. It challenges traditional centralized models by empowering networks to operate through shared resources, collective decision-making, and unified user experiences. This foundational shift paves the way for systems that are more resilient, secure, and transparent, making them ideal for applications ranging from finance to data storage.
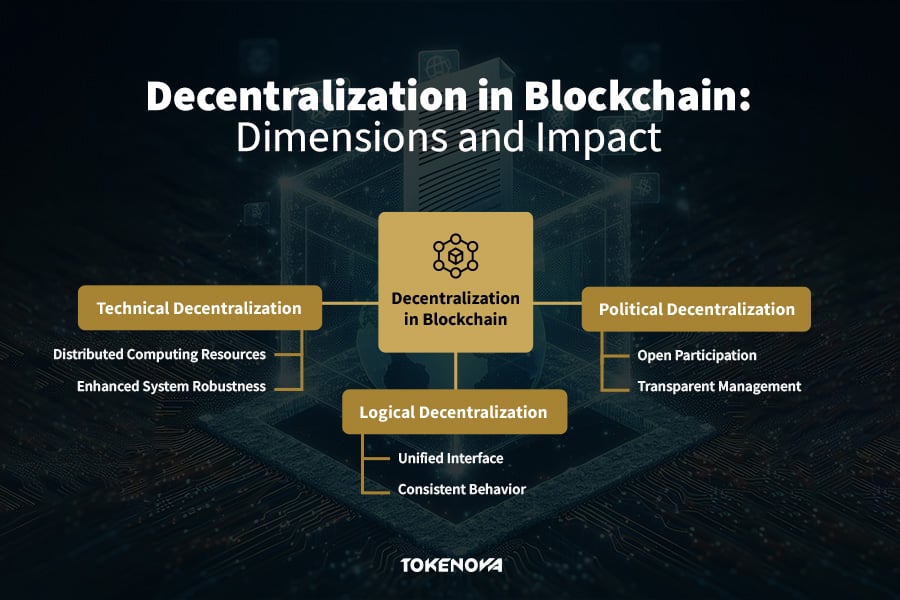
Technical Decentralization
Technical decentralization refers to the physical and infrastructural aspects of a blockchain network. It involves distributing computing resources, data storage, and processing power across numerous nodes. This approach minimizes the risks associated with centralized failures and enhances the overall system robustness.
Political Decentralization
Political decentralization focuses on distributing governance and decision-making authority among network participants. This dimension is crucial for ensuring that no single entity can dominate the network’s operations or impose arbitrary changes. It supports open, democratic participation and transparent management of the blockchain.
Did You Know? Over 1,000 active DAOs exist as of 2025, managing assets totaling over $25 billion collectively.
Logical Decentralization
Logical decentralization addresses the user experience and how a blockchain system presents itself as a cohesive entity. Despite being built on a network of independently operating nodes, a decentralized blockchain typically offers a unified interface and consistent behavior, which is vital for usability and reliability.
Did You Know? Bitcoin has approximately 20,000 nodes across 93 countries, while Ethereum has around 5,922 nodes in 81 countries. This makes them among the most decentralized blockchains.
Technical Decentralization: Distributed Infrastructure
Technical decentralization in blockchain is all about creating a robust, distributed network that can withstand failures and attacks. By spreading the operational load across many nodes, the system avoids single points of failure, which are common in centralized systems.

Before delving into specific aspects, it is important to note that technical decentralization not only provides security but also ensures the continuous availability of services. This robustness is achieved through redundancy, distributed consensus, and geographically diverse node distribution.
Network Resilience and Redundancy
One of the cornerstones of technical decentralization is network resilience. In a decentralized blockchain, thousands of nodes work together, each maintaining a complete copy of the ledger. This redundancy means that if one or several nodes go offline or are compromised, the overall network continues functioning without interruption. The system’s fault tolerance is a direct result of this dispersed architecture, which makes it exceedingly difficult for attackers to target a single point of failure.
Geographical Dispersion and Security
The physical distribution of nodes across different regions is another key aspect of technical decentralization. Geographical dispersion mitigates risks related to localized disruptions, such as natural disasters, power outages, or regulatory interventions. By ensuring that nodes are spread over diverse regions, decentralization enhances overall security. An attacker would need to compromise a significant number of nodes in various locations simultaneously to impact the network—a scenario that is both logistically and economically unfeasible.
Consensus Mechanisms
Consensus mechanisms are vital for maintaining the integrity of a decentralized blockchain. Whether through proof-of-work (PoW), proof-of-stake (PoS), or other innovative methods, these protocols distribute the responsibility of validating transactions among many independent participants. This collective verification process prevents any single entity from controlling the addition of new blocks to the ledger. By enabling decentralized agreement, consensus mechanisms are fundamental to ensuring that all nodes work in harmony and that the blockchain remains secure and transparent.
Did You Know? Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus reduces energy consumption by over 99.99% compared to PoW, making it a greener alternative.
Political Decentralization: Distributed Governance and Control
Political decentralization in blockchain shifts the power dynamics from a central authority to a network of users. This democratic approach to governance is essential for ensuring that no single party can dictate the evolution or operation of the network.

Prior to exploring the subtopics, it is useful to understand that political decentralization underpins the autonomy and fairness of blockchain systems. By enabling distributed decision-making, blockchain networks can resist censorship, promote inclusivity, and support an open environment for protocol upgrades and governance.
Shared Decision-Making
At the heart of political decentralization is shared decision-making. In a decentralized blockchain, governance is not concentrated in the hands of a few; instead, every participant has the opportunity to influence protocol changes and network upgrades. This inclusive approach helps prevent the centralization of power and ensures that all voices are heard. As a result, blockchain networks can evolve organically, with consensus-driven decisions that reflect the collective interests of the community.
Transparent Governance Models
Transparent governance is a key component of political decentralization. Blockchain platforms often implement both on-chain and off-chain governance models to facilitate open dialogue and decision-making. On-chain governance allows token holders to vote on proposals directly within the blockchain system, while off-chain discussions in community forums and public meetings provide additional layers of transparency. This dual approach fosters trust among participants and ensures that the network’s evolution is guided by a clear, democratic process.
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs)
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) represent a groundbreaking application of political decentralization. DAOs operate through smart contracts that automatically execute decisions based on collective voting outcomes. These organizations eliminate the need for a traditional management hierarchy, empowering community members to oversee operations, manage funds, and initiate projects.
Logical Decentralization: Unified System Behavior
Logical decentralization is about the coherence and user experience of a blockchain system. While the underlying infrastructure is highly distributed, the system appears unified and consistent to its users.

Before we break down the specifics, consider that logical decentralization ensures that users interact with a single, cohesive system, despite the network’s distributed nature. This unification is critical for usability and trust, as it provides a familiar interface and consistent behavior regardless of the complexities happening behind the scenes.
Seamless User Experience
A seamless user experience is one of the primary goals of logical decentralization. Although a blockchain operates across thousands of independent nodes, it presents a uniform ledger to its users. This means that every participant, regardless of their location or the node they connect to, sees the same data and transaction history. The consistency in user experience is vital for ensuring that the system is accessible and reliable, even as it benefits from the robustness of a decentralized architecture.
Balancing Independence and Cohesion
Logical decentralization requires a careful balance between the independence of individual nodes and the cohesion of the overall system. While each node operates autonomously, the blockchain must ensure that all parts of the network remain synchronized and coherent. This balance is achieved through sophisticated synchronization protocols and consensus mechanisms that align the behavior of disparate nodes. The result is a network that is both resilient and easy to use, providing a unified experience while still harnessing the benefits of decentralization in blockchain.
Hybrid Models
Some blockchain platforms adopt hybrid models that blend logical centralization with underlying decentralization. For example, while smart contracts on a network like Ethereum execute uniformly across all nodes—creating a centralized feel from the user perspective—the validation process remains decentralized. These hybrid models offer the advantages of both worlds: a consistent and predictable user interface alongside the security and resilience provided by a distributed network.
Types of Decentralization in Blockchain
Blockchain deecntralization is best understood as a spectrum rather than a binary state. Various blockchain networks exhibit different degrees of decentralization, each balancing technical, political, and logical factors in unique ways.
Before diving into the specific types, it is essential to recognize that the level of decentralization for any blockchain is determined by its design choices, consensus protocols, governance models, and overall network structure. This nuanced perspective allows stakeholders to assess and compare different systems more accurately.
Full vs. Partial Decentralization

Full decentralization is achieved when a blockchain maximizes its distributed infrastructure, governance, and unified system behavior. Systems like Bitcoin exemplify this approach by ensuring that every node operates independently and that all decisions are made collectively. On the other hand, partial decentralization involves trade-offs. Some blockchain networks may sacrifice complete decentralization to improve performance, scalability, or regulatory compliance. For example, permissioned blockchains restrict node participation to approved entities, offering a balance between decentralization and operational efficiency. Understanding these differences is crucial when evaluating the suitability of a blockchain for specific applications.
Evaluating Decentralization Levels
Evaluating how much a blockchain is decentralized requires considering several key factors. The choice of consensus mechanism—whether it be proof-of-work, proof-of-stake, or delegated systems—directly affects how power is distributed among participants. Additionally, the geographic distribution of nodes, the transparency of governance models, and the distribution of native tokens all contribute to the overall degree of decentralization. A well-distributed token supply and an open, inclusive governance process are indicators of a highly decentralized network. Stakeholders must weigh these factors carefully to determine the true extent of decentralization in blockchain systems.
Benefits of Decentralization in Blockchain
Decentralization offers transformative benefits that extend far beyond technical improvements. By eliminating centralized control, these systems create environments that are more secure, transparent, and innovative.
Before exploring specific benefits, it is important to appreciate that the advantages of decentralization are interlinked. Enhanced security leads to greater trust, while transparency fosters accountability. Together, these factors drive efficiency and open up new avenues for innovation and participation.
- Enhanced Security and Fault Tolerance
One of the most significant benefits of a decentralized blockchain is its enhanced security. By spreading data and processing across a vast network of nodes, the risk of system-wide failures is dramatically reduced. This redundancy makes it extremely difficult for attackers to compromise the network. For instance, in consensus models like proof-of-work, an attacker would need to control a substantial portion of the network’s resources to alter the ledger—a task that becomes increasingly infeasible as the network grows. This inherent fault tolerance ensures that decentralized systems remain operational and secure, even when individual nodes fail.
- Increased Transparency and Trust
Since every transaction is recorded on a public ledger accessible to all network participants, the system fosters an environment of accountability and trust. This transparency not only deters fraudulent activities but also enables real-time auditing and verification. With all actions visible and traceable, stakeholders can confidently rely on the network’s integrity, eliminating the need for traditional intermediaries and their associated risks.
- Reduced Censorship and Improved Freedom
By design, decentralization in blockchain reduces the risk of censorship and unilateral control. Without a central authority capable of imposing restrictions, blockchain networks empower users with greater financial and informational freedom. This censorship resistance is particularly valuable in regions with stringent regulatory controls or where political pressures might otherwise limit access to services. In decentralized systems, users maintain control over their own data and assets, thereby reinforcing personal autonomy and digital sovereignty.
- Operational Efficiency and Cost Reduction
Decentralization streamlines operations by eliminating the need for numerous intermediaries that traditionally slow down processes and drive up costs. Blockchain networks can operate continuously—24/7—without the constraints of conventional business hours. Smart contracts automate many processes, reducing administrative overhead and error-prone manual intervention. These efficiencies translate into lower transaction fees and faster processing times, making decentralized systems particularly attractive for global commerce and micro-payment solutions.
Did You Know? Blockchain transactions can reduce cross-border payment costs by up to 40%, thanks to fewer intermediaries and faster settlement times.
- Driving Innovation and Open Access
By removing gatekeepers and lowering barriers to entry, decentralized systems create an open environment where developers and entrepreneurs can experiment freely. This permissionless landscape has led to groundbreaking innovations in areas such as decentralized finance (DeFi), non-fungible tokens (NFTs), and decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs). The collaborative nature of open-source development further accelerates progress, ensuring that decentralization continues to drive creative solutions and new business models across industries.
The Spectrum of Decentralization
Blockchain decentralization is best understood as a dynamic continuum where varying levels of distributed control coexist. Different projects exhibit different degrees of decentralization based on their design, operational goals, and trade-offs with other system attributes such as scalability and regulatory compliance.
Before examining the spectrum in detail, it is important to recognize that achieving complete decentralization in every aspect is often impractical. Instead, blockchain networks aim to optimize decentralization in areas where it yields the greatest benefits, while sometimes accepting compromises in others to meet specific performance or compliance goals.
Balancing Trade-offs
Blockchain designers must carefully balance the trade-offs between decentralization and other critical system attributes. For example, while a fully decentralized network maximizes security and transparency, it may face challenges in scalability or speed. Conversely, systems that are partially centralized might offer enhanced performance but at the cost of increased vulnerability to single points of failure. Understanding these trade-offs is essential for determining the appropriate level of decentralization for a given application. Stakeholders must assess the risks and benefits associated with each approach to ensure that the chosen design aligns with the intended use case and long-term goals.
Continuous Improvement
Decentralization in blockchain is not a static goal but an ongoing process of refinement and adaptation. As technology evolves and user needs change, blockchain networks continually seek to enhance their degree of decentralization. This process involves expanding node distribution, refining governance models, and developing new consensus mechanisms that better distribute power. Continuous improvement is essential for maintaining the resilience and security of decentralized systems, ensuring that they remain robust in the face of emerging challenges and threats.
Real-World Applications of Decentralization in Blockchain
By leveraging decentralized principles, organizations can create systems that are more secure, transparent, and resistant to centralized control, thereby driving innovation and expanding access. Each application is tailored to meet particular needs and challenges, showcasing the flexibility and transformative potential of decentralized technology.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) is one of the most visible and impactful applications of decentralization. DeFi platforms enable users to engage in financial activities, such as lending, borrowing, and trading, without relying on traditional banks or financial institutions. By utilizing smart contracts, these platforms facilitate automated, trustless transactions that occur around the clock.
DeFi innovations have given rise to decentralized exchanges (DEXs), where users can trade cryptocurrencies directly from their wallets. This model reduces counterparty risk and improves liquidity by eliminating the need for centralized intermediaries. In addition, lending protocols allow for peer-to-peer borrowing and lending, creating new opportunities for individuals to access financial services without cumbersome credit checks or excessive fees.
Read More: Future of Decentralized Finance: The Upcoming Financial Revolution
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs)
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) are a revolutionary application of political decentralization in blockchain. DAOs empower communities to govern themselves without the need for traditional hierarchical structures. Operated through smart contracts, these organizations allow members to propose initiatives, vote on decisions, and manage funds collectively.
DAOs are transforming how projects are managed by enabling a more democratic and transparent decision-making process. This governance model not only reduces the potential for corruption but also fosters innovation by allowing diverse groups of stakeholders to collaborate on shared goals.
Decentralized Data Storage
Decentralized data storage solutions offer a robust alternative to traditional cloud storage services. Systems such as the InterPlanetary File System (IPFS) and Filecoin distribute data across a network of nodes, rather than relying on centralized servers. This approach increases data security and redundancy, ensuring that information remains accessible even if individual nodes fail.
By dispersing data across multiple locations, decentralized storage solutions reduce the risk of censorship and data loss. Users benefit from lower costs and enhanced privacy, as no single entity controls the entire dataset. This innovative approach to data management not only challenges the dominance of traditional cloud providers but also aligns with the broader goals of data sovereignty and digital freedom.
Conclusion
Decentralization in blockchain is a transformative force that redefines the digital landscape. By distributing technical infrastructure, governance, and system behavior, decentralized networks offer unprecedented security, transparency, and efficiency. Embracing this multi-dimensional approach paves the way for innovative applications that empower users and drive sustainable digital growth. As industries continue to evolve, the principles of decentralized blockchains will remain at the forefront of technological progress, fostering a more open, resilient, and inclusive future.
For organizations looking to implement decentralized solutions, Tokenova offers comprehensive tokenization solutions and blockchain consultation services to help navigate the complexities of this revolutionary technology. Contact our experts today to explore how decentralization can transform your business operations.











