Imagine a world where you have complete control over your finances—no banks dictating terms, no intermediaries taking a cut, just you, and a transparent system that operates seamlessly across the globe. This isn’t a distant dream; it’s the reality that Decentralized Finance (DeFi) is creating right now.
Decentralized Finance, commonly known as DeFi, is more than just a buzzword in the tech and finance industries; it’s a transformative movement that’s redefining how we interact with money. By leveraging the power of blockchain technology, DeFi aims to democratize finance, breaking down barriers and making financial services accessible to anyone with an internet connection. In an era where traditional financial systems are often criticized for their inefficiencies, lack of transparency, and exclusivity, DeFi emerges as a beacon of innovation and empowerment.
This comprehensive guide delves deep into the definition of Decentralized Finance (DeFi), exploring its core principles, key components, and the revolutionary impact it’s having on the global financial landscape. Whether you’re a seasoned investor looking to diversify your portfolio or a curious newcomer eager to understand this groundbreaking phenomenon, this article is your gateway to the future of finance. We’ll explore not just what DeFi is, but how it works, the benefits and risks associated with it, and the potential it holds for transforming economies worldwide.
First Things First: What Is Decentralized Finance (DeFi)?
Decentralized Finance, or DeFi, represents a paradigm shift in the way financial services are structured and delivered. At its essence, DeFi is an open, permissionless, and highly interoperable financial ecosystem built on blockchain technology, particularly Ethereum. Unlike traditional finance, which relies heavily on centralized institutions like banks, brokerages, and insurance companies, DeFi leverages decentralized networks to facilitate financial transactions and services without intermediaries.
Definition and Core Principles
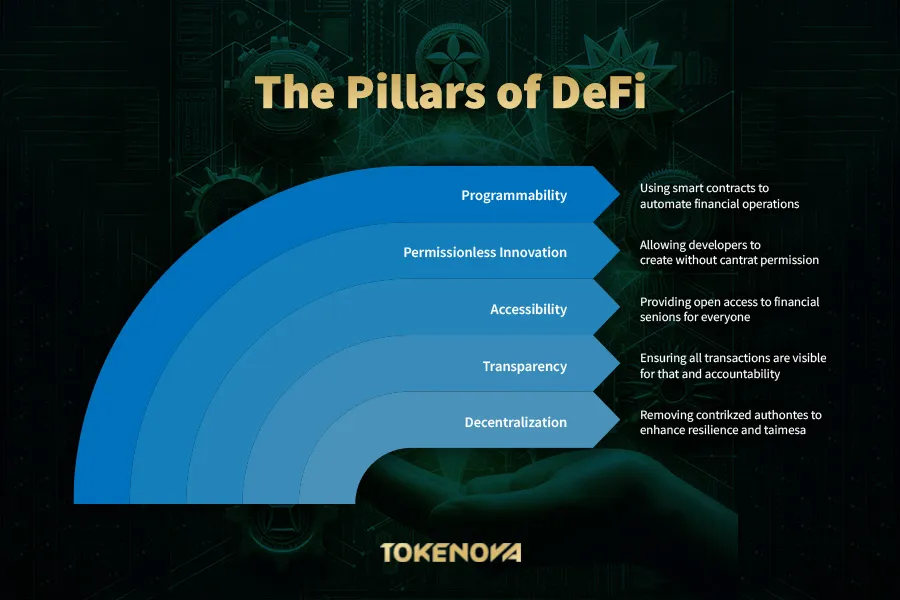
DeFi is an umbrella term for a variety of financial applications in cryptocurrency or blockchain geared toward disrupting financial intermediaries. It embodies a set of principles that aim to make financial systems more accessible, transparent, and efficient. The core principles of DeFi include:
- Decentralization: At the heart of DeFi is the removal of centralized authorities. Transactions and operations are conducted on decentralized platforms where no single entity has control. This decentralization ensures that the system is not vulnerable to a single point of failure and promotes resilience and fairness.
- Transparency: All transactions and smart contract codes are visible on the blockchain. This transparency allows for public scrutiny, which fosters trust and accountability within the system. Users can verify transactions themselves without needing to rely on third-party audits or reports.
- Accessibility and Open Access: DeFi platforms are designed to be accessible to anyone with an internet connection. There are no gatekeepers or stringent requirements to access financial services, making it inclusive for people across different geographies and socio-economic backgrounds.
- Permissionless Innovation: Developers can build on DeFi protocols without seeking permission from a central authority. This openness encourages innovation and the development of new financial products and services that can interoperate seamlessly.
- Programmability: DeFi leverages smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. This programmability enables the automation of complex financial operations and the creation of new financial instruments.
By adhering to these principles, DeFi aims to create a more inclusive, efficient, and transparent financial ecosystem that empowers individuals and fosters innovation. efficient, and transparent financial ecosystem that empowers individuals and fosters innovation.
Read More: Future of Decentralized Finance: The Upcoming Financial Revolution
How Does DeFi Compare to Traditional Financial Systems?
To fully grasp the significance of DeFi, it’s crucial to compare it with traditional financial systems, often referred to as centralized finance (CeFi). In traditional finance, financial services are provided by centralized institutions like banks, insurance companies, and stock exchanges. These institutions act as intermediaries, facilitating transactions between parties and often imposing fees, rules, and regulations that can limit access and efficiency.

Centralization vs. Decentralization: Traditional finance is centralized, meaning that control and decision-making authority resides with a central entity. In contrast, DeFi operates on decentralized networks where control is distributed among participants. This decentralization reduces the risk of systemic failures and corruption associated with centralized systems.
Accessibility: Traditional financial services often have barriers to entry, such as minimum account balances, credit checks, and geographical limitations. DeFi platforms eliminate these barriers, offering services to anyone regardless of their financial status or location.
Transparency and Trust: In traditional finance, operations are typically opaque, with little visibility into how decisions are made or how funds are managed. DeFi’s transparency allows users to see exactly how protocols function and how their funds are being used, reducing the need to trust third parties.
Cost and Efficiency: Intermediaries in traditional finance can introduce inefficiencies and additional costs due to fees and slower transaction times. DeFi removes intermediaries, leading to faster transactions and lower fees, enhancing overall efficiency.
Innovation and Flexibility: DeFi’s open-source nature allows for rapid innovation and the creation of new financial products. Traditional finance is often constrained by regulations and legacy systems that can hinder innovation.
In essence, DeFi doesn’t just replicate traditional financial services on a digital platform; it reimagines them to be more accessible, transparent, and user-centric, addressing many of the shortcomings inherent in traditional financial systems.
Key Components of Decentralized Finance
Understanding DeFi requires an in-depth look at its foundational elements, which work together to create a cohesive and innovative financial ecosystem. The key components of DeFi include smart contracts, decentralized applications (DApps), and blockchain technology. Let’s take a look at each in detail:
Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are the backbone of DeFi. They are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code, which exists across a distributed, decentralized blockchain network. Smart contracts automatically enforce and execute transactions when predefined conditions are met, without the need for intermediaries or manual intervention.
Functionality: Smart contracts facilitate, verify, and enforce the negotiation or performance of a contract. They can handle the exchange of money, property, shares, or anything of value in a transparent and conflict-free manner.
Security and Immutability: Once a smart contract is deployed on the blockchain, its code cannot be changed. This immutability ensures that the contract’s terms cannot be tampered with, providing security and trust in the execution of agreements.
Automation: Smart contracts automate complex processes, reducing the potential for human error and increasing efficiency. For example, in a lending agreement, a smart contract can automatically release funds when collateral is provided, and enforce repayment terms without the need for a bank to oversee the transaction.
Smart contracts are revolutionizing how agreements are formed and executed, reducing reliance on traditional legal systems and intermediaries.
Read More: Token Burning: Is Your Crypto Going Up in Smoke?
Decentralized Applications (DApps)
Decentralized Applications, or DApps, are applications that run on a decentralized network, utilizing smart contracts to function without centralized control. DApps combine a user interface with smart contracts to provide a seamless experience for users engaging with DeFi services.
Open Source: Most DApps are open-source, allowing developers to build upon existing applications, fostering innovation, and collaboration within the community.
User Control: DApps enable users to interact directly with the blockchain, maintaining control over their data and assets without relying on centralized servers or authorities.
Interoperability: DApps can interoperate with other applications and services within the DeFi ecosystem, enabling the creation of complex financial products and services.
💡Uniswap for decentralized trading, Compound for lending and borrowing, and MakerDAO for stablecoin issuance are some of the well-known DeFi DApps in the market right now.(source)
Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology is the foundational infrastructure upon which DeFi operates. It is a distributed ledger technology that records transactions across a network of computers, ensuring transparency, security, and immutability.
Decentralization: Blockchain operates on a peer-to-peer network where each participant maintains a copy of the ledger. This decentralization eliminates the need for a central authority and reduces the risk of single points of failure.
Security and Immutability: Transactions recorded on the blockchain are secured using cryptographic techniques, making them tamper-proof. Once data is recorded, it cannot be altered, ensuring the integrity of the ledger.
Transparency: All transactions are publicly visible, allowing for auditability and trust among participants.
Consensus Mechanisms: Blockchain networks use consensus algorithms, such as Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS), to validate transactions and maintain the integrity of the network.
💡Blockchain technology not only underpins the DeFi ecosystem but also provides the tools necessary for creating a transparent and secure financial system that operates without intermediaries.
How Does DeFi Work?
Decentralized Finance operates by utilizing blockchain technology and smart contracts to facilitate financial services in a decentralized manner. By removing intermediaries and leveraging automation, DeFi provides an alternative to traditional financial systems that is more accessible, efficient, and transparent.
Mechanisms of Peer-to-Peer Transactions
At the core of DeFi is the ability to conduct peer-to-peer (P2P) transactions without the need for intermediaries like banks or brokers. This is achieved through the use of smart contracts and decentralized platforms that connect users directly.
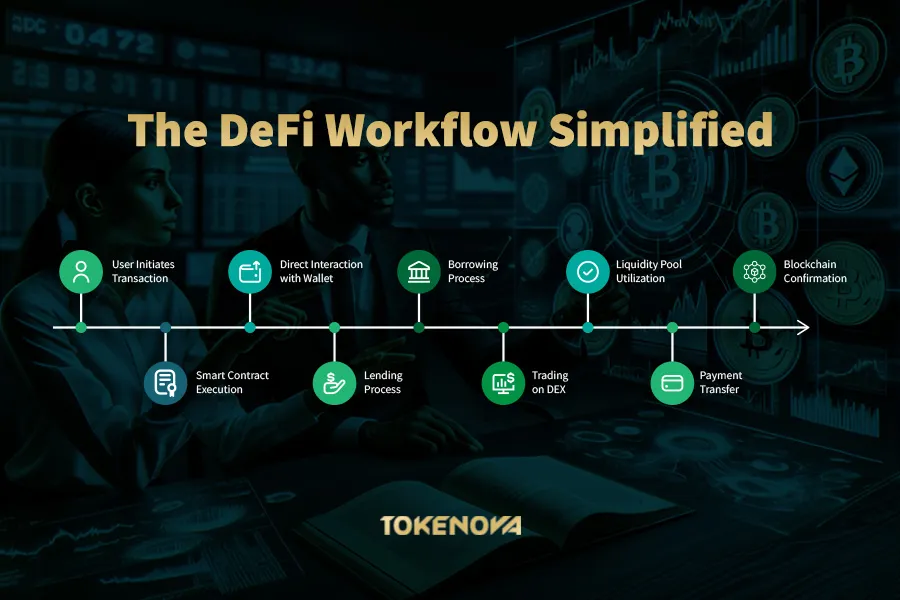
Direct Interaction: Users interact directly with DeFi platforms using cryptocurrency wallets, such as MetaMask, which allow them to manage their assets securely. Transactions are executed through smart contracts, which automatically enforce the terms of the agreement.
Lending and Borrowing: In DeFi lending platforms, users can lend their assets to others and earn interest, while borrowers can access funds by providing collateral. Smart contracts handle the terms, interest rates, and repayment schedules without human intervention.
Trading: Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) enable users to trade cryptocurrencies directly from their wallets. DEXs use liquidity pools and automated market makers to facilitate trades without order books or centralized control.
Payments and Remittances: DeFi platforms allow for instant and low-cost transfers of funds globally, bypassing traditional payment networks and reducing fees associated with cross-border transactions.
By enabling peer-to-peer transactions, DeFi empowers individuals to have full control over their financial activities, reducing dependency on traditional institutions.
Common Usages of DeFi
The versatility of DeFi has led to the development of a wide array of applications that replicate and enhance traditional financial services in a decentralized context. These applications are transforming how individuals and businesses interact with financial systems.
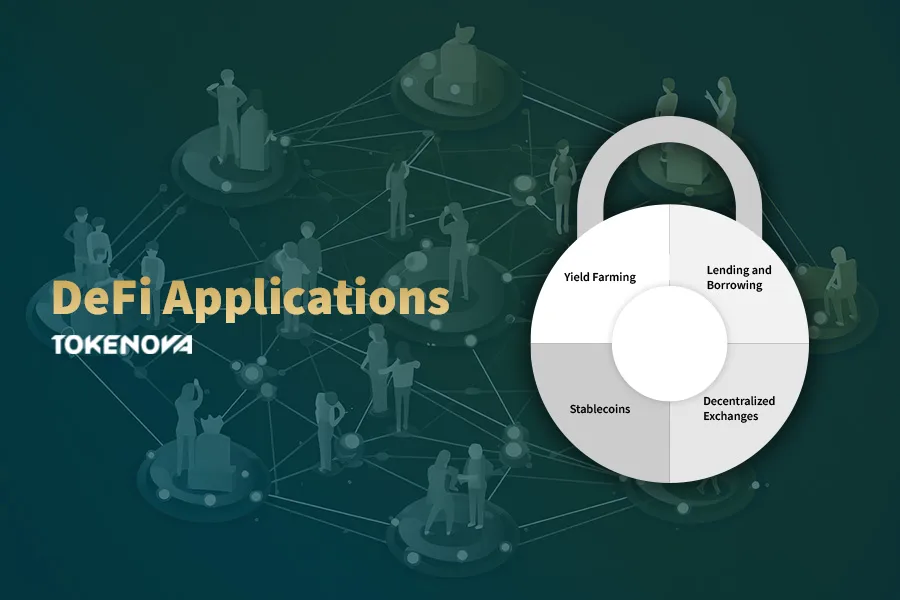
Lending and Borrowing Platforms
DeFi lending platforms, such as Aave and Compound, allow users to lend their cryptocurrencies to earn interest or borrow assets by providing collateral.
Lending: Users deposit their assets into a liquidity pool. The platform uses these pooled assets to provide loans to borrowers. Lenders earn interest on their deposits, which can often be higher than traditional savings accounts due to the demand for borrowing.
Borrowing: Borrowers can access loans by providing collateral, usually in the form of other cryptocurrencies. The loan-to-value ratio and interest rates are determined by the platform’s protocols. Smart contracts manage the terms and enforce repayment.
Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs)
Decentralized exchanges, such as Uniswap and SushiSwap, enable users to trade cryptocurrencies directly from their wallets without the need for a centralized intermediary.
Read More: How to Build a Crypto Exchange
Automated Market Makers (AMMs): DEXs use AMMs to set the price of assets through algorithms based on the ratio of tokens in liquidity pools. This removes the need for order books and allows for continuous trading.
Liquidity Provision: Users can provide liquidity to pools by depositing pairs of tokens. In return, they receive a portion of the trading fees generated by the platform.
Non-Custodial Trading: Users maintain control of their assets at all times, reducing the risk of exchange hacks and loss of funds.
💡DEXs democratize trading by lowering barriers to entry and enhancing security compared to centralized exchanges.
Stablecoins
Stablecoins are cryptocurrencies designed to minimize price volatility by pegging their value to a stable asset, such as fiat currencies or commodities.
Fiat-Collateralized Stablecoins: These are backed by reserves of fiat currency held by a central entity. Examples include Tether (USDT) and USD Coin (USDC).
Crypto-Collateralized Stablecoins: Backed by other cryptocurrencies and managed through smart contracts. MakerDAO’s DAI is a prominent example, where users lock up ETH as collateral to generate DAI.
Algorithmic Stablecoins: Use algorithms and smart contracts to manage the supply and maintain price stability without direct collateralization.
💡Stablecoins bridge the gap between traditional finance and the crypto world, offering stability and reliability in transactions.
Yield Farming and Liquidity Mining
Yield farming involves staking or lending crypto assets to generate high returns or rewards in the form of additional cryptocurrency. Liquidity mining is a subset where users provide liquidity to DeFi protocols and receive tokens as rewards.
Yield Farming: Users move their assets across various DeFi platforms to maximize returns. They earn interest, fees, or governance tokens, depending on the platform’s incentives.
Liquidity Mining: By providing liquidity to a platform, users are rewarded with the platform’s native tokens. These tokens can often be traded or used within the platform for governance.
💡Yield farming and liquidity mining have become popular ways for users to generate passive income but require a thorough understanding of the associated risks.
Benefits of Decentralized Finance

DeFi offers numerous advantages that address many limitations of traditional financial systems. These benefits contribute to its growing popularity and adoption across the globe.
Financial Inclusion
One of the most significant benefits of DeFi is its ability to provide financial services to individuals who are unbanked or underbanked.
Accessibility: DeFi platforms are accessible to anyone with an internet connection, regardless of their geographic location or socio-economic status. There are no requirements for identification documents, credit history, or minimum account balances.
Empowerment: Individuals gain full control over their assets and financial decisions. DeFi eliminates the dependency on centralized institutions, empowering users to manage their finances independently.
Economic Development: By providing access to financial services, DeFi can stimulate economic activity in regions where traditional banking infrastructure is lacking, contributing to poverty reduction and economic growth.
💡DeFi has the potential to democratize finance, making it more inclusive and equitable.
Reduced Costs and Fees
DeFi reduces or eliminates many of the fees associated with traditional financial services by removing intermediaries.
Lower Transaction Fees: Transactions conducted on DeFi platforms often have lower fees compared to traditional banking transactions, which may include charges for transfers, currency conversions, and account maintenance.
Efficiency: Automated processes and smart contracts streamline operations, reducing operational costs and the potential for human error.
Competitive Interest Rates: DeFi platforms often offer more attractive interest rates for both lenders and borrowers due to the efficiencies gained from decentralization.
Enhanced Transparency
Transparency is a cornerstone of DeFi, fostering trust and accountability within the financial ecosystem.
Open Ledger: All transactions are recorded on the blockchain and are publicly accessible. Users can verify transactions and monitor the flow of funds.
Auditability: The transparent nature of DeFi allows for easier auditing and compliance verification, which can reduce fraud and corruption.
Informed Decision-Making: Users have access to all relevant information about protocols, including smart contract code and transaction histories, enabling them to make informed decisions.
Accessibility and Open Access
DeFi platforms operate without the constraints of traditional financial institutions, offering services that are always available.
24/7 Availability: DeFi services are not bound by business hours or holidays. Users can conduct transactions and access services at any time.
Permissionless Entry: There are no gatekeepers in DeFi. Users do not need approval or face discrimination based on their background, nationality, or credit history.
Global Reach: DeFi transcends borders, allowing users from different countries to participate in the same financial ecosystem without currency or regulatory barriers.
Popular DeFi Platforms and Protocols
The DeFi landscape is rich with innovative platforms and protocols that offer a variety of financial services. Understanding these platforms can provide insight into how DeFi operates and its potential applications.
Uniswap
Uniswap is a decentralized exchange that allows users to trade cryptocurrencies without intermediaries.
Automated Market Maker (AMM): Uniswap uses an AMM model, where liquidity pools are used instead of traditional order books. Prices are determined by a constant product formula, balancing the ratio of tokens in a pool.
Liquidity Provision: Users can become liquidity providers by depositing pairs of tokens into pools. In return, they earn a portion of the trading fees generated by the platform.
Token Swapping: Uniswap supports a wide range of ERC-20 tokens, enabling seamless swapping between different cryptocurrencies.
Uniswap revolutionized decentralized trading by simplifying the process and making it accessible to all users.
Aave
Aave is a DeFi protocol for lending and borrowing cryptocurrencies.
Flash Loans: Aave introduced flash loans, which are uncollateralized loans that must be repaid within the same transaction. They enable complex arbitrage and liquidation strategies.
Interest Rate Options: Users can choose between stable and variable interest rates, providing flexibility based on market conditions.
Diverse Asset Support: Aave supports a wide range of cryptocurrencies, allowing users to lend and borrow various assets.
Innovative features like flash loans have set Aave apart as a leader in DeFi lending platforms.
MakerDAO
MakerDAO is known for creating DAI, a decentralized stablecoin.
DAI Stablecoin: DAI is pegged to the US dollar and maintains its stability through smart contracts and collateralized debt positions (CDPs).
Collateralized Debt Positions: Users lock up Ethereum or other approved assets as collateral to generate DAI. The system manages the collateralization ratio to maintain stability.
Governance: Holders of the MKR token participate in governance, making decisions about protocol changes, risk parameters, and collateral types.
MakerDAO provides a stable medium of exchange in the DeFi ecosystem, essential for various financial activities.
Tokenova: Your Partner in DeFi Solutions
In the rapidly evolving world of Decentralized Finance, navigating the complexities and opportunities can be challenging. Tokenova stands as a trusted partner, offering expertise and tailored solutions to help individuals and businesses embrace DeFi confidently.
✅Comprehensive Tokenization Services: Tokenova specializes in transforming assets into digital tokens, unlocking new opportunities for investment, liquidity, and ownership. This process enables fractional ownership and global accessibility.
✅Regulatory Compliance: Navigating the regulatory landscape is crucial in DeFi. Tokenova provides guidance to ensure compliance with relevant laws and regulations, mitigating legal risks.
✅Customized Strategies: Understanding that each client has unique needs, Tokenova develops personalized strategies to align with specific goals, whether entering DeFi, launching a new project, or expanding services.
✅Technological Innovation: Leveraging cutting-edge blockchain technology, Tokenova ensures efficient, secure, and scalable solutions that are future-proof and adaptable to the evolving DeFi landscape.
With Tokenova, you can confidently navigate the DeFi ecosystem, transforming your financial operations and staying ahead in the digital economy.
Contact Tokenova today to unlock the full potential of Decentralized Finance and be part of the financial revolution.
Future of Decentralized Finance
The future of DeFi is promising, with numerous trends and innovations poised to drive its growth and integration into mainstream finance.
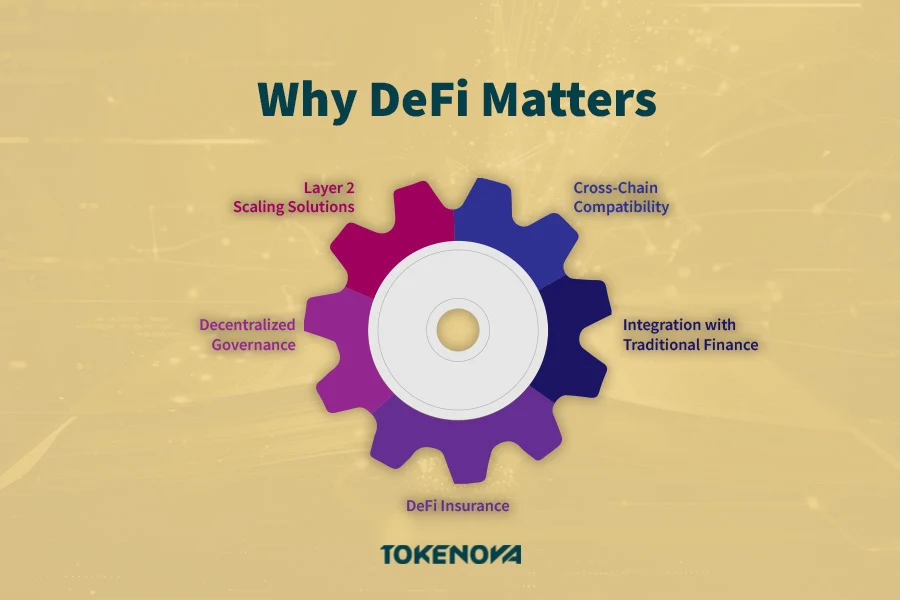
Emerging Trends and Innovations
Layer 2 Scaling Solutions: Technologies like Optimistic Rollups and zk-Rollups aim to improve blockchain scalability by processing transactions off-chain and settling them on-chain. These solutions can significantly reduce fees and increase transaction speeds.
Cross-Chain Compatibility: Projects like Polkadot and Cosmos are working towards enabling interoperability between different blockchains. This cross-chain compatibility can expand DeFi’s reach and allow for more complex and integrated financial products.
Decentralized Governance: Increased emphasis on community governance models empowers users to have a say in protocol development and management, fostering greater alignment between stakeholders.
Integration with Traditional Finance: There’s a growing trend of DeFi platforms collaborating with traditional financial institutions, potentially leading to hybrid models that combine the strengths of both systems.
DeFi Insurance: Platforms offering insurance against smart contract failures and hacks are emerging, providing an added layer of security for users.
Read More: Ultimate Guide to Smart Contract Security
Potential Impact on Global Financial Systems
Disruption of Traditional Banking: DeFi has the potential to disrupt traditional banking services by offering more efficient, accessible, and user-centric alternatives. Banks may need to adapt by adopting blockchain technology and integrating DeFi principles.
Economic Empowerment: By providing financial services to the unbanked and underbanked, DeFi can contribute to reducing global inequality and promoting economic growth in developing regions.
Regulatory Transformation: Governments and regulatory bodies may need to develop new frameworks to accommodate decentralized systems, potentially leading to more progressive and adaptive regulations.
Innovation in Financial Products: DeFi enables the creation of new financial instruments and services that were not possible within traditional frameworks, such as programmable money, decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs), and tokenized assets.
Read More: Tokenization in Banking: Transforming the Financial Landscape
💡The influence of DeFi could lead to a more inclusive, efficient, and innovative global financial system, transforming how financial services are delivered and consumed.
Pro Tips: Mastering DeFi with Confidence
“Your Roadmap to DeFi Success”
Embarking on your DeFi journey can be both exciting and challenging. Here are some pro tips to help you navigate this new landscape confidently and effectively.
Educate Yourself Continuously
Knowledge is your most valuable asset in the rapidly evolving DeFi space.
- Stay Informed: Regularly read articles, follow reputable DeFi news outlets, and subscribe to newsletters to keep up with the latest developments.
- Understand the Fundamentals: Gain a solid understanding of blockchain technology, smart contracts, and the specific platforms you plan to use.
- Engage with the Community: Participate in forums, attend webinars, and join social media groups to learn from experienced users and developers.
Continuous learning will help you make informed decisions and stay ahead in the dynamic DeFi environment.
Start Small and Diversify
Managing risk is crucial when dealing with volatile assets and new technologies.
- Experiment Cautiously: Begin by investing small amounts to familiarize yourself with different platforms and services without exposing yourself to significant risk.
- Diversify Your Investments: Spread your assets across multiple DeFi platforms and tokens to reduce the impact of any single point of failure.
- Set Clear Objectives: Define your investment goals and risk tolerance to guide your strategies.
Diversification and cautious experimentation can enhance your potential returns while mitigating risks.
Prioritize Security
Protecting your assets should be a top priority in DeFi.
- Use Secure Wallets: Opt for hardware wallets like Ledger or Trezor for long-term storage and significant holdings.
- Enable Security Measures: Implement two-factor authentication and use strong, unique passwords for all your accounts.
- Beware of Scams: Always verify URLs, double-check addresses, and be cautious of unsolicited communications.
Taking proactive steps to secure your assets can prevent losses due to hacks or fraud.
Understand the Risks
Being aware of potential pitfalls and web3 risks allows you to take appropriate precautions.
- Smart Contract Risks: Recognize that smart contracts can have vulnerabilities. Use platforms that have undergone thorough audits.
- Market Volatility: Prepare for price fluctuations and only invest amounts you can afford to lose.
- Regulatory Risks: Stay informed about legal developments in your country that may affect DeFi activities.
An informed approach to risk management can safeguard your investments and ensure a smoother experience.
Utilize Tools and Resources
Leverage available technologies to enhance your DeFi activities.
- Portfolio Management: Use applications like Zapper or DeBank to track your investments and returns across different platforms.
- Yield Optimization: Platforms like Yearn.finance can help maximize returns by automatically moving funds to the most profitable opportunities.
- Educational Platforms: Resources like DeFiPulse and CoinGecko offer valuable data and insights into the DeFi market.
Utilizing tools can streamline your activities and help you make more strategic decisions.
💡Pro Tip: Always test new platforms and strategies with minimal funds to assess their functionality and risks before committing larger amounts.
Conclusion
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) represents a groundbreaking shift in the way we perceive and interact with financial systems. By leveraging blockchain technology and smart contracts, DeFi offers a more inclusive, transparent, and efficient alternative to traditional finance. It empowers individuals by granting them control over their assets and financial decisions, breaking down barriers that have long limited access to financial services.
Throughout this exploration of the Decentralized Finance (DeFi) definition, we’ve delved into its core principles, key components, and the innovative applications that are reshaping the financial landscape. While DeFi holds immense promise, it’s essential to approach it with a balanced perspective, acknowledging the risks and challenges alongside the opportunities.
As DeFi continues to evolve, it has the potential to foster economic growth, promote financial inclusion, and drive innovation in ways we are only beginning to understand. Whether you’re an investor, developer, or simply curious about the future of finance, engaging with DeFi offers a chance to be part of a transformative movement that could redefine global economic systems.
Embrace the possibilities that DeFi offers, but do so with knowledge, caution, and a commitment to continuous learning. The revolution in finance is not just about technology; it’s about creating a fair and open system that benefits everyone.
Key Takeaways
- DeFi Defined: Decentralized Finance (DeFi) is an open, global financial system built on blockchain technology, eliminating intermediaries and offering a more inclusive and transparent alternative to traditional finance.
- Core Components: Smart contracts, decentralized applications (DApps), and blockchain technology form the foundational infrastructure of DeFi.
- Benefits: DeFi offers financial inclusion, reduced costs, enhanced transparency, and accessibility, empowering individuals worldwide.
- Risks: Participants should be aware of security vulnerabilities, regulatory uncertainty, market volatility, and scalability issues inherent in DeFi.
- Popular Platforms: Uniswap (decentralized exchange), Aave (lending and borrowing), and MakerDAO (stablecoin issuance) are leading platforms offering unique services within the DeFi ecosystem.
- Future Outlook: Innovations like layer 2 scaling solutions, cross-chain compatibility, and integration with traditional finance point toward DeFi’s growing influence and potential to reshape global financial systems.
- Pro Tips: Success in DeFi involves continuous education, starting small, prioritizing security, understanding risks, and utilizing available tools and resources.
Engaging with DeFi equips you to be part of a financial revolution that emphasizes empowerment, innovation, and inclusivity, reshaping our world one transaction at a time.
references: Investopedia, Coinbase, Britannica
1. Can DeFi Replace Traditional Banking Systems Entirely?
While Decentralized Finance has the potential to significantly disrupt traditional banking by offering alternative services, it’s unlikely to replace it entirely in the near future. DeFi addresses many limitations of traditional finance, such as accessibility and efficiency, but also faces challenges like scalability, regulatory compliance, and widespread user adoption. Traditional banks may adapt by integrating blockchain technology and DeFi principles into their services, potentially leading to a hybrid financial system that combines the strengths of both models.
2. How Do I Choose a Reliable DeFi Platform?
Selecting a trustworthy DeFi platform involves thorough research and due diligence. Consider the following factors:
Team and Development: Investigate the backgrounds of the team members and developers behind the project. A transparent and experienced team adds credibility.
Security Audits: Ensure that the platform has undergone independent security audits by reputable firms to identify and mitigate vulnerabilities.
Community Feedback: Engage with the community through forums and social media to gather insights and reviews from other users.
Transparency: Trustworthy platforms are transparent about their protocols, updates, and governance structures.
Liquidity and Volume: Higher liquidity and transaction volumes can indicate a healthy and active platform.
By carefully evaluating these aspects, you can minimize risks and choose platforms that align with your investment goals and risk tolerance.
3. What Is the Role of Governance Tokens in DeFi?
Governance tokens are integral to the decentralized nature of many DeFi protocols. They grant holders the right to participate in the decision-making processes of the platform.
Voting Rights: Holders can vote on proposals affecting the protocol, such as changes to fees, introduction of new features, or adjustments to risk parameters.
Incentives: Governance tokens often come with incentives, such as a share of the platform’s revenue or additional rewards for active participation.
Alignment of Interests: By involving users in governance, platforms align the interests of the community with the success and sustainability of the protocol.
Decentralization: Governance tokens distribute control among a broad base of users, reducing the influence of any single entity and promoting democratic management.
Owning governance tokens allows you to have a direct impact on the future development and direction of DeFi projects you support.










