Forget the fragile handshakes and ambiguous clauses of traditional agreements. Step into a realm where contracts are not just words on paper, but self-executing code, meticulously etched onto the immutable ledger of blockchain. Instead a world where trust is not a hopeful aspiration, but a verifiable certainty, baked into the very fabric of every transaction. This is the transformative promise of smart contracts on the blockchain, a technology poised to redefine how we conduct business and interact in the digital age.
Are you weary of the inefficiencies of outdated systems, the ever-present specter of human error, and the costly layers of intermediaries that erode value? Prepare to be enlightened. This exploration delves into the profound benefits of smart contracts in blockchain, dissecting their intricate mechanisms and illuminating their disruptive potential across diverse industries. We will unveil the compelling advantages of leveraging blockchain smart contracts, demonstrating why understanding and implementing them is no longer optional, but a strategic imperative for forward-thinking organizations.
From streamlining complex financial operations to revolutionizing global supply chains, we will unpack the multifaceted applications of smart contracts in blockchain, equipping you with the insights to grasp and capitalize on this groundbreaking innovation. Envision replacing uncertainty with unshakeable digital logic, ensuring every agreement is flawlessly executed, every single time. This paradigm shift in building trust and fostering reliable collaboration is the essence of the smart contract revolution, and its impact is only just beginning to be realized.
Introduction: Blockchain Smart Contracts
Imagine a tireless, incorruptible digital assistant that flawlessly carries out tasks. That’s what a smart contract is — like a high-tech vending machine for complex agreements and assets.
You input the right conditions (e.g., a payment), and it automatically delivers the result (like ownership transfer). These self-executing contracts are coded instructions stored on the blockchain— a transparent, tamper-proof ledger — making them virtually unhackable and highly trustworthy.

Definition
At their essence, smart contracts are autonomous digital agreements that execute automatically once specific conditions are met. Think of them as precise “if-then” code logic brought to life on the blockchain—like a sensor-triggered system that activates based on temperature. This automation eliminates the need for intermediaries, ensuring that agreements are enforced impartially and flawlessly, delivering fairness and transparency without human involvement.
Mechanism
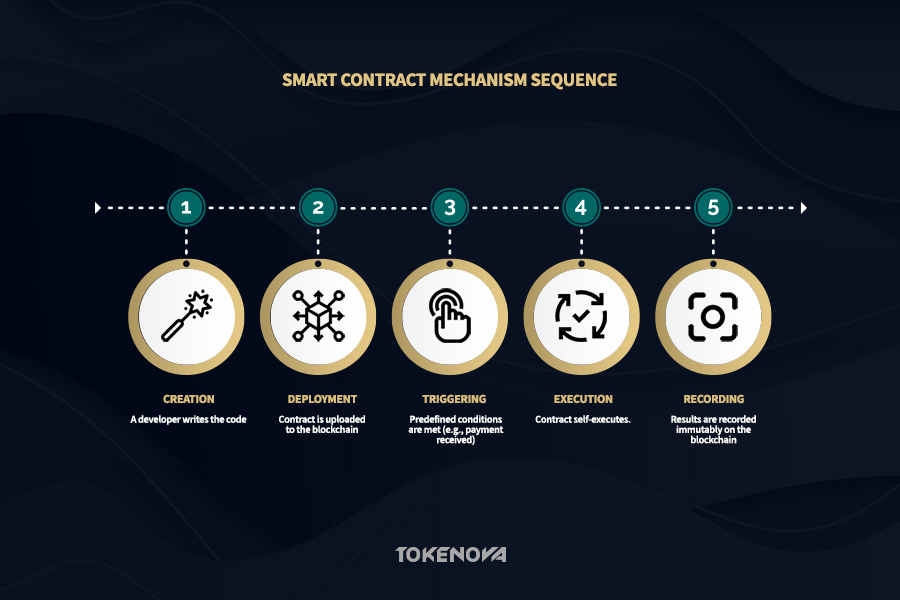
The true power of smart contracts lies in their deep integration with blockchain technology. Once created, a smart contract is given a unique digital identity and distributed across a decentralized network of nodes. This decentralization ensures no single entity can alter or control the contract, making it highly resistant to tampering or failure.
When the contract’s conditions are met—like a payment or delivery—the network verifies the event and records the transaction immutably on the blockchain. This creates a transparent, permanent, and auditable record, forming the foundation of the trust and reliability that define smart contracts.
Evolution
The concept of a “smart contract” dates back to 1994, when visionary computer scientist Nick Szabo first proposed self-executing digital agreements. Yet, it wasn’t until Ethereum’s revolutionary debut in 2015—with its powerful Solidity language—that this vision found fertile ground. This pivotal moment unlocked a surge of innovation, finally enabling the real-world application of smart contracts and unveiling the transformative benefits of smart contracts in blockchain—efficiency, automation, and trust—on a global scale.
Core Attributes: What Makes Smart Contracts Unique
Several fundamental attributes elevate smart contracts from a mere concept to a disruptive force. A deep understanding of these core characteristics is essential to fully appreciate the transformative advantages of smart contracts in blockchain.
Automation
Benefits of Smart Contracts include seamless automation that executes agreements with precision and without human error. Once conditions are met, the contract self-activates, eliminating delays and biases. For example, in a decentralized prediction market, smart contracts automatically distribute rewards based on verified outcomes. This tireless, impartial automation drives efficiency and minimizes operational friction, embodying a core advantage of blockchain-based agreements.
Immutability & Transparency
Picture the blockchain as a digital ledger carved in stone — unchangeable and permanent. Once a smart contract is recorded, its code becomes immutable, even to its creators, ensuring the terms remain fixed and trustworthy. Paired with full public visibility of both the code and its execution history, this transparency empowers all parties to independently verify outcomes. Together, immutability and transparency form a foundation of trust, making smart contracts a powerful tool for verifiable, tamper-proof agreements.
Intermediary Elimination
One of the most compelling benefits of smart contracts lies in their ability to eliminate intermediaries—legal professionals, brokers, and notaries—who traditionally add cost, complexity, and delay. By automating these roles through self-executing code, smart contracts reduce transaction costs, streamline operations, and boost efficiency. This “trustless execution” redefines how trust is built, making the impartial logic of code the new standard in reliable agreements.
Read More: Blockchain Governance: Building Trust and Transparency
Key Benefits: Why Smart Contracts Are Transformative
Now, let’s delve into the core value proposition that makes smart contracts such a compelling technology. The undeniable benefits of smart contracts in blockchain are the primary forces driving their accelerating adoption across a vast spectrum of industries.
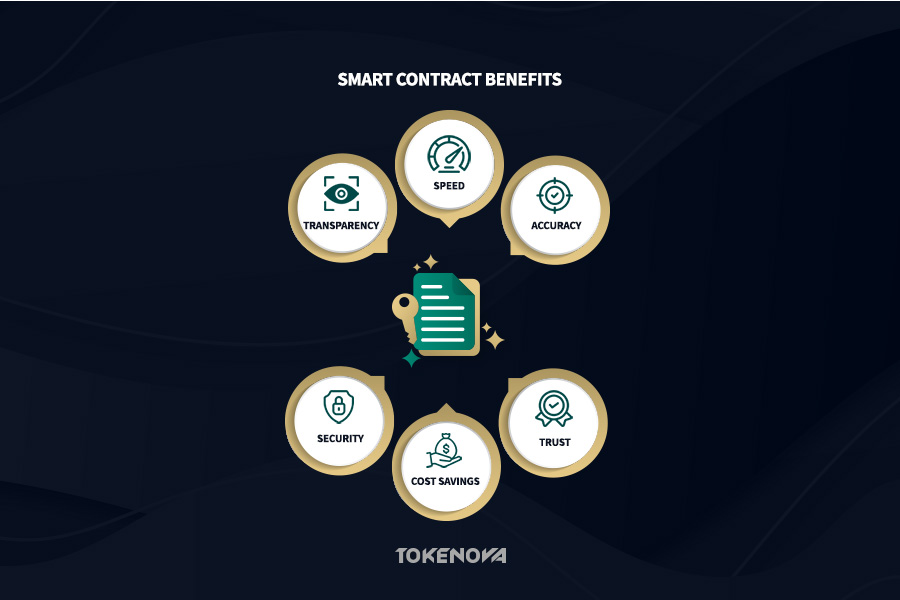
Transparency: Fostering Verifiable Agreements
Imagine agreements as open books — fully accessible, verifiable, and tamper-proof. This is the transparency smart contracts bring, with code and transaction histories immutably recorded on the blockchain. In decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs), for instance, everything from governance rules to treasury management becomes auditable and trusted. This radical transparency, a core benefit of smart contracts, is shown to reduce disputes by up to 40%, streamlining operations and strengthening relationships.
Accuracy: Minimizing Human Error
Human error—a common flaw in manual processes—often leads to costly mistakes in traditional agreements. Smart contracts, driven by the precise logic of code, virtually eliminate these risks. Once predefined conditions are met, execution is flawless, leaving no room for ambiguity or misinterpretation. This level of accuracy is especially valuable in high-volume or complex transactions, where even small errors can have major consequences.
Speed: Accelerating Transaction Velocity
Bid farewell to the delays and red tape of traditional processes. Thanks to their built-in automation, smart contracts dramatically speed up execution. For example, securities trades that once took days can now settle in minutes or seconds—eliminating intermediaries and unlocking major capital efficiencies. Among the key Benefits of Smart Contracts, this acceleration stands out as a powerful edge for forward-thinking businesses.
Cost Savings: Reducing Transactional Friction
Benefits of Smart Contracts include the streamlined elimination of intermediaries, leading to dramatic cost reductions. By automating manual processes and cutting out expensive third parties, they significantly lower fees, reduce administrative burdens, and limit the risk of costly legal disputes. Experts estimate these efficiencies can slash transaction costs by 10% to 50%, depending on the use case and complexity involved.
Security: Leveraging Cryptographic Integrity
One of the core benefits of smart contracts lies in their exceptional security, rooted in the cryptographic strength of blockchain technology. Once deployed, a smart contract becomes virtually tamper-proof, safeguarded by advanced encryption and distributed consensus. This makes unauthorized alterations nearly impossible, offering a powerful layer of protection—especially valuable in sectors dealing with sensitive data and high-stakes transactions.
Trust: Algorithmic Enforcement of Agreements
Benefits of Smart Contracts include fostering a new era of trust by replacing reliance on intermediaries and subjective judgment with the precise, impartial execution of code. This incorruptible logic ensures agreements are enforced exactly as intended, enabling confident transactions—even between parties with no prior trust. It’s this shift toward verifiable digital certainty that’s driving smart contract adoption across diverse sectors.
Efficiency: Streamlining Operational Workflows
Benefits of Smart Contracts include streamlining operations by automating manual tasks and eliminating paperwork. This increased efficiency enables businesses to be more agile, reduce administrative load, and focus resources on innovation. For instance, smart contracts can cut insurance claim processing times from weeks to days, enhancing customer satisfaction and allowing staff to handle more complex cases.
Sustainability: Enabling Digital Agreements
While older blockchains raise energy concerns, the benefits of smart contracts extend to environmental sustainability by reducing paper use, storage needs, and carbon emissions. As energy-efficient proof-of-stake networks grow, smart contracts offer a greener path for digital commerce.
Versatility: Diverse Application Landscape
The remarkable adaptability of smart contracts is truly astounding. Their potential applications span a vast and ever-expanding array of industries, from the transformative world of decentralized finance (DeFi) and the intricate complexities of supply chain management to the sensitive realm of healthcare, the traditionally cumbersome processes of real estate, and even the fundamental aspects of digital identity management. This broad applicability unequivocally underscores the transformative potential of this groundbreaking technology and vividly highlights the numerous and diverse uses of smart contracts in blockchain.
Use Cases: Real-World Applications of Smart Contracts
The compelling benefits of smart contracts in blockchain are not confined to theoretical discussions; they are actively being deployed and demonstrating their transformative power in a multitude of real-world applications across diverse sectors.
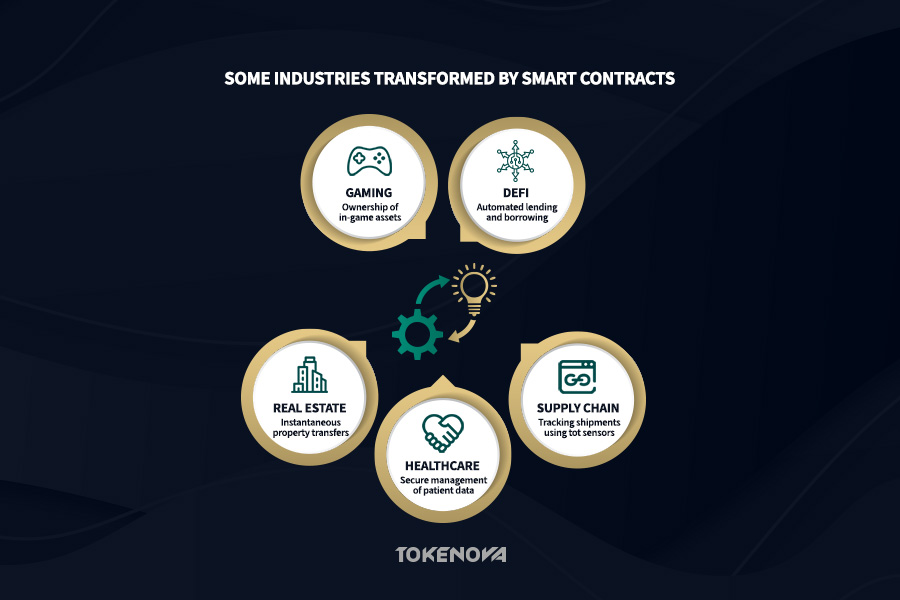
DeFi: Automating Financial Services
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) serves as a shining example of smart contracts moving from concept to impactful reality. Imagine a financial system operating without the need for traditional banks or financial institutions. Automated lending and borrowing platforms, decentralized exchanges (DEXs) facilitating peer-to-peer trading, and innovative yield farming protocols all heavily rely on the precise and automated execution of smart contracts to ensure transparent and efficient operations.
For instance, lending platforms utilize smart contracts to automatically manage loan collateral, seamlessly distribute interest payments to lenders, and efficiently execute liquidations when borrowers fail to meet their obligations. As of early, 2025, the Total Value Locked (TVL) in decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols stands at approximately $125.787 billion, according to DefiLlama.
This marks a significant recovery from the lows experienced in December 2022, when TVL dropped to under $40 billion. The resurgence in TVL can be attributed to factors such as the Federal Reserve’s interest rate cuts in late 2024, which have revitalized investor interest in DeFi platforms.
Read More: DeFi Loan Mechanisms: Crypto Lending Explained
Supply Chain: Enhancing Traceability & Efficiency
Imagine a world where every step of a product’s journey—from raw material to final delivery—is tracked with absolute clarity and speed. Smart contracts are revolutionizing supply chain management by enabling automated payments the moment shipments are verified via IoT sensors. This level of automation not only boosts transparency but also slashes disputes and streamlines operations. Industry data confirms that implementing blockchain-based supply chain systems driven by smart contracts can yield substantial cost reductions—highlighting one of the most impactful benefits of smart contracts.
Healthcare: Securing Patient Data & Streamlining Processes
The healthcare industry, with its strict privacy and security demands, stands to benefit greatly from smart contracts. By securely storing patient data on the blockchain and granting access only under pre-defined conditions, smart contracts enhance data security, protect patient privacy, and streamline processes like insurance claim handling. They’re also being used to manage patient consent, ensuring compliance with regulations such as HIPAA. This automation reduces administrative overhead, accelerates reimbursements, and ultimately improves efficiency for both patients and providers—showcasing the transformative benefits of smart contracts in healthcare.
Read More: Exploring the 10 Types of Smart Contracts in Blockchain
Real Estate: Simplifying Property Transactions
The traditionally complex real estate process is primed for transformation through the benefits of smart contracts, offering unparalleled efficiency and transparency. Envision a future where property ownership transfers and fund releases occur automatically once all conditions are verifiably met—eliminating stressful escrow delays and reducing fraud risk. Beyond this, smart contracts are enabling fractional ownership models, where multiple parties can seamlessly co-own property, with rights and revenue transparently managed by code. This marks a revolutionary shift in real estate investment accessibility and trust.
Read More: Fractional Investment in Tokenized Real Estate Assets
Gaming: Enabling True Digital Ownership
The dynamic gaming industry is harnessing the benefits of smart contracts and NFTs to revolutionize player experiences. These technologies empower gamers with true ownership of digital assets—rare items or virtual land—that can be freely traded across platforms. Smart contracts ensure authenticity and secure transactions, forming the backbone of digital asset management.
Play-to-earn models further highlight the benefits of smart contracts, enabling players to earn cryptocurrency through in-game achievements. With billions in NFT trading volume, smart contracts are unlocking powerful new economic models and transforming digital ownership across gaming and beyond.

Challenges: Obstacles to Overcome
While the numerous benefits of smart contracts in blockchain are undeniable and their potential vast, it’s crucial to acknowledge the existing challenges and consider the exciting possibilities that lie ahead.
Scalability & Energy Consumption
One of the primary hurdles facing widespread smart contract adoption is the inherent scalability limitations of certain blockchain networks, particularly those utilizing older “proof-of-work” consensus mechanisms. Imagine a digital highway struggling to handle peak traffic that’s the essence of the scalability challenge. Furthermore, some of these earlier blockchain technologies require significant amounts of energy to operate, raising valid environmental concerns. However, the blockchain community is actively developing and implementing innovative solutions to address these issues Ethereum successfully completed its transition to Proof-of-Stake (PoS) with The Merge on September 15, 2022.
This upgrade reduced Ethereum’s energy consumption by approximately 99.95% (arstechnica), making it significantly more environmentally friendly. The network now relies on validators instead of miners, drastically lowering its carbon footprint. In addition, “layer-2” scaling solutions, such as Optimistic Rollups (e.g., Arbitrum, Optimism) and ZK-Rollups (e.g., zkSync, StarkNet), have seen substantial adoption by January 2025.
These technologies have collectively processed billions of transactions, effectively reducing gas fees and enhancing scalability for Ethereum-based applications. For instance, Arbitrum — a leading Layer 2 optimistic rollup for Ethereum — surpassed 1 billion transactions within just three years of its mainnet launch in August 2021.
Legal & Regulatory Frameworks

The legal and regulatory landscape surrounding smart contracts is still in its formative stages, presenting both opportunities and challenges. Fundamental questions regarding the legal enforceability of smart contracts, the determination of jurisdiction in the event of cross-border disputes, and the allocation of liability in case of code vulnerabilities are actively being debated and analyzed by legal scholars, policymakers, and industry stakeholders worldwide.
regulatory clarity around smart contracts has significantly advanced across various jurisdictions. The European Union’s Markets in Crypto-Assets (MiCA) regulation became fully applicable (sumsub) on December 30, 2024, establishing a unified framework for crypto assets and smart contracts within the EU.
In the United States, the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) announced the formation of a dedicated cryptocurrency task force on January 21, 2025, aiming to develop a comprehensive regulatory framework for digital assets. This initiative reflects a shift from previous enforcement-based approaches, with the task force working in coordination with other federal agencies and international counterparts to provide clearer guidelines for the crypto industry.
This lack of clear and consistent legal and regulatory frameworks across different jurisdictions remains a significant hurdle to overcome for the widespread and seamless adoption of smart contracts on a global scale. It’s akin to navigating uncharted waters without a reliable map.
Read More: Asset Tokenization Regulation: Navigating Compliance in 2025
Security Vulnerabilities
Despite the many benefits of smart contracts, their security remains a critical concern. Due to blockchain’s immutability, once a vulnerable contract is deployed, fixing it is difficult—making thorough testing and auditingessential. Common threats like reentrancy attacks and integer overflows highlight the need for rigorous safeguards. Fortunately, the industry is advancing tools and best practices, including formal verification and enhanced security audits, to address these challenges.

Future Trends: The Road Ahead
While the numerous benefits of smart contracts in blockchain are undeniable and their potential vast, it’s crucial to acknowledge the existing challenges and consider the exciting possibilities that lie ahead.
AI & IoT Integration
The benefits of smart contracts are rapidly expanding through their integration with AI and IoT, ushering in a new era of intelligent automation. By 2025, AI is enhancing smart contracts with advanced clause analysis, dispute resolution, and anomaly detection, increasing accuracy and compliance. In supply chains, AI and blockchain synergy enables predictive analytics and data-driven decisions, while IoT sensors automate actions like payments based on real-time data. This convergence streamlines operations, reduces fraud, and minimizes manual oversight. Looking ahead, AI will further empower smart contracts with nuanced decision-making and complex process automation—solidifying their role in transforming industries.
Hybrid Contract Models
While the benefits of smart contracts are vast, it’s unlikely they’ll fully replace traditional legal agreements. A more realistic path forward lies in hybrid models—blending the automation of smart contracts with the nuanced interpretation and legal certainty of traditional frameworks. In this model, smart contracts handle well-defined, automatable tasks, while complex legal matters remain under conventional oversight, offering a balanced fusion of innovation and legal reliability.
Scalability Solutions
The ongoing development and implementation of various scalability solutions are crucial for the widespread adoption of smart contracts. Layer-2 solutions like rollups, sidechains, and state channels are designed to increase transaction throughput and reduce fees on main blockchain networks. These solutions enable more complex and high-volume applications of smart contracts, making them viable for a broader range of use cases.
Regulatory Advancements
As the understanding and adoption of smart contracts grow, regulatory frameworks are expected to mature and provide clearer guidelines for their use. This includes the development of legal standards for smart contract enforceability, cross-border recognition, and consumer protection. Clearer regulations will foster greater confidence and encourage wider adoption of smart contracts across industries.
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs)
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs), which rely heavily on smart contracts for their governance and operations, are expected to become more prevalent. DAOs offer new models for organizational structure and decision-making, enabling more transparent and community-driven initiatives. In 2024, Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) have continued to expand, with entities like Uniswap DAO and Aave DAO managing substantial assets. Uniswap’s treasury, for instance, holds nearly $5.3 billion, predominantly in UNI tokens.
Interoperability Between Blockchains
The ability for different blockchain networks to communicate and interact with each other, known as interoperability, is a key area of development. Interoperability solutions will enable smart contracts on different blockchains to work together, unlocking new possibilities for cross-chain applications and data sharing.
Pro Tips: Optimizing Smart Contract Implementation
Deploying smart contracts effectively requires precision, security, and adaptability. Here’s a concise guide to optimize your implementation:
1. Plan with Precision
- Clearly define the contract’s logic and conditions.
- Map out all possible scenarios, including edge cases, before coding.
- Use flowcharts or pseudocode to visualize the contract’s behavior.
2. Test Thoroughly
- Conduct unit tests for individual functions and integration tests for system-wide compatibility.
- Perform stress tests to evaluate performance under high loads.
- Use frameworks like Truffle or Hardhat for Ethereum-based contracts.
3. Prioritize Security
- Engage third-party auditors to identify vulnerabilities like reentrancy attacks or integer overflows.
- Use automated tools like Slither or MythX for code analysis.
- Implement bug bounty programs to crowdsource vulnerability detection.
4. Stay Compliant
- Monitor evolving regulations like the EU’s MiCA or U.S. state laws.
- Consult legal experts to ensure enforceability, especially for cross-border contracts.
- Design contracts with regulatory requirements in mind.
5. Choose the Right Platform
- Select a blockchain platform based on your needs: Ethereum for robust functionality, Polygon for scalability, or Binance Smart Chain for lower fees.
- Consider trade-offs between public, private, and consortium blockchains.
- Evaluate the platform’s ecosystem, including developer tools and community support.
6. Optimize for Efficiency
- Minimize gas costs by reducing expensive operations like storage writes and loops.
- Use Layer-2 solutions (e.g., Arbitrum, Optimism) to lower transaction fees.
- Employ gas-efficient coding patterns, such as packing variables into storage slots.
7. Enable Safe Upgrades
- Use proxy patterns to separate logic from data storage, allowing for future upgrades.
- Implement pausable contracts to halt functionality in emergencies.
- Control upgrades via multi-signature wallets or decentralized governance to prevent misuse.
8. Document Clearly
- Add detailed comments in the code to explain complex logic.
- Provide a user guide for interacting with the contract.
- Maintain a changelog to track updates and modifications.
9. Use Reliable Oracles
- Integrate trusted oracle networks like Chainlink for secure off-chain data.
- Ensure data is tamper-proof and verified to prevent manipulation.
- Include fallback mechanisms in case of oracle failures.
10. Monitor Post-Deployment
- Use blockchain explorers and monitoring tools to track contract activity.
- Set up alerts for unusual transactions or behavior.
- Regularly update dependencies and review contract performance.
Conclusion
The compelling and multifaceted benefits of smart contracts in blockchain represent a profound paradigm shift in how agreements are conceived, executed, and ultimately enforced. Offering unprecedented levels of transparency, operational efficiency, robust security, and unwavering trust, smart contracts are poised to revolutionize a vast array of industries, from the intricate workings of global finance and the complexities of supply chain management to the sensitive domain of healthcare and beyond.
While legitimate challenges such as scalability limitations and the evolving regulatory landscape persist, the transformative potential of this groundbreaking technology is undeniable, and its continued evolution promises to unlock even greater levels of innovation, automation, and efficiency across the global economy. Understanding the significant and far-reaching advantages of blockchain smart contracts is no longer merely an option;
it is rapidly becoming a strategic imperative for businesses, organizations, and even individuals seeking to not only navigate but also thrive in an increasingly digital and interconnected world. The fundamental question is no longer *if* smart contracts will impact your domain, but rather *how* you will strategically leverage their immense power to gain a competitive edge, foster innovation, and build a more trustworthy and efficient future.
Key Takeaways
- Smart contracts are self-executing digital agreements immutably encoded on a blockchain, automating processes and eliminating the need for traditional intermediaries.
- Key benefits include significantly enhanced transparency, unparalleled accuracy in execution, lightning-fast transaction speeds, substantial cost savings, robust security underpinned by cryptography, and a new paradigm of trust built on code.
- Real-world applications are rapidly proliferating across diverse sectors, including decentralized finance (DeFi), supply chain management, healthcare, real estate, and the burgeoning world of blockchain gaming.
- While challenges such as scalability limitations on certain blockchain networks and the evolving nature of legal and regulatory frameworks persist, significant progress is being made to address these hurdles through ongoing technological advancements and proactive policy development.
- The future of smart contracts holds immense promise, with exciting possibilities arising from their integration with Artificial Intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT), paving the way for even more sophisticated and autonomous applications.
References:
Blockchain-based Smart Contracts: A Systematic Mapping Study of Academic Research (2018)
Smart Contracts in Blockchain Technology: A Critical Review
Blockchain-Enabled Smart Contracts: Architecture, Applications, and Future Trends
How do smart contracts handle disputes?
Smart contracts are designed to execute automatically based on predefined conditions, minimizing the potential for disputes. However, if disagreements arise, parties can use oracle networks like Chainlink to verify external data and ensure accuracy. Additionally, arbitration mechanisms can be built into the contract, allowing a trusted third party to resolve conflicts. In jurisdictions where smart contracts are legally recognized, parties can also rely on existing legal frameworks to enforce agreements or resolve disputes.
What measures prevent vulnerabilities in smart contract code?
Preventing vulnerabilities in smart contract code requires a multi-layered approach. Rigorous testing using tools like Truffle or Hardhat is essential to identify and fix bugs. Security audits conducted by third-party firms can uncover issues such as reentrancy attacks or integer overflows. Formal verification methods can mathematically prove the correctness of the code, ensuring it behaves as intended. Additionally, bug bounty programs can incentivize external developers to find and report vulnerabilities, further strengthening the contract’s security.
Can smart contracts be used for personal agreements?
Yes, smart contracts can be used for personal agreements. For example, they can automate rental agreements by handling rent payments and deposit releases based on predefined conditions. They can also manage loan agreements, enforcing repayment terms and interest calculations without manual intervention. Shared expenses, such as splitting costs among roommates or group members, can also be streamlined using smart contracts. However, it is important to ensure that the contract is legally enforceable in the relevant jurisdiction and that all parties fully understand and agree to the terms.