In the ever-evolving world of finance, tokenization is emerging as a game-changer, particularly within the banking sector. This innovative process involves converting rights to an asset into a digital token, which can be traded on a blockchain. As we delve into the intricacies of tokenization in banking, we’ll explore its mechanisms, benefits, challenges, and future potential, all while weaving in personal insights and anecdotes to keep the journey engaging.
Introduction to Tokenization in Banking
Tokenization, at its core, is the process of converting sensitive data into a unique identifier, or token, that retains essential information without compromising security. In the context of modern finance, tokenization is revolutionizing how banks handle assets, transactions, and customer data. Historically, the concept of tokenization has roots in the banking sector, where it began as a method to enhance security and efficiency in financial transactions.

How Tokenization Works in General
Understanding the mechanics of tokenization in banking is crucial. The process begins with identifying the asset or data to be tokenized. This could range from real estate to customer information. Once identified, the asset is assigned a digital token, which is stored on a blockchain. This token acts as a stand-in for the actual asset, allowing for secure and efficient transactions.
Types of Tokens Related to Banking
- Utility Tokens: These are used within banking services to facilitate transactions and access specific services. They are not backed by physical assets but serve as a medium of exchange within a particular ecosystem.
- Security Tokens: These represent ownership in an asset, such as stocks or real estate, and are used in asset-backed financing and investments. They offer investors a digital representation of their ownership rights.
Benefits of Tokenization in Banking
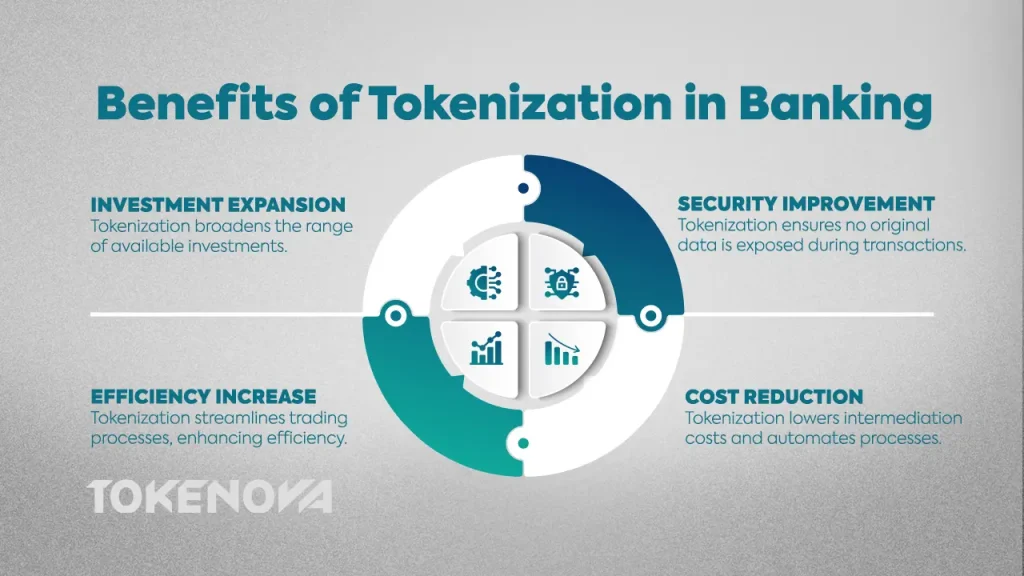
Tokenization gives a wide array of advantages that are already changing the banking landscape. On the same note, security has been improved perhaps by far by the fact that through tokenization, no original information is ever released during any transaction. Thirdly, tokenization reduces intermediation costs and increases efficiency by eliminating long processes in the trading of securities. Through this strategy, the overall costs at the banks can be slashed since many operations can be automated easily. Furthermore, tokenization brings illiquidity into the now-liquid world by tokenizing it and expanding the range of available investments.
Banking Tokenization Key Statistics
In the first half of 2024, as reported by PYMNTS Article, there were over 22 billion tokenized transactions, marking a 49% increase compared to the previous year. This highlights the rapid adoption and scaling of tokenization in the banking and financial sectors, underscoring its role in enhancing transaction security and efficiency.
| Statistic | Figure | Description |
| Number of Tokenized Transactions | 22 billion (H1 2024) | Represents the volume of tokenized transactions in the first half of 2024. |
| Year-over-Year Transaction Increase | 49% | Shows the growth rate in tokenized transactions compared to the same period in the previous year. |
Tokenization in banking is experiencing significant growth, as evidenced by the 22 billion transactions recorded in the first half of 2024. This surge, a 49% increase from the previous year, illustrates how banks are leveraging tokenization to enhance security and streamline operations. The substantial uptake in tokenized transactions demonstrates the banking sector’s confidence in tokenization as a robust solution for managing sensitive data and executing faster, more secure transactions. This trend indicates that tokenization is not just a passing phase but a foundational shift toward more secure and efficient financial ecosystems.
Tokenization for banking is not a trendy use of technology but a potent phenomenon that continually shapes banking integration at large. In the following sections, the multifaceted advantages that it offers are presented.
- Enhanced Security
As threats in cyberspace increase, improving the safeguards of financial actions is the utmost necessity. Tokenization can achieve this by substituting the original value of items like credit card numbers and bank account numbers with fictional values referred to as tokens. That in return decreases the possibility of experiencing losses through fraud or having private information revealed to unauthorized parties. Since the actual data is stored in a different area that is inaccessible to the outside world (often called the token safe) if tokens are seized, they have no value. This level of security is especially important in the fight against fraud because it minimizes the transfer of sensitive information to various ecosystems.
- Transaction Efficiency
In this context, the use of blockchain technology reduces the time for tokens through tokenization. The decentralized nature of Blockchain implies real-time transaction processing and settlement without requiring third-party involvement. It also cuts down the transaction time and at the same time, it brings about fewer chances of making mistakes and repetition. Such intermediaries as clearinghouses and other financial intermediaries are thus reduced leading to efficiencies that will allow bank and customer transactions to be executed at a fraction of the time it was normally expected to take depending on circumstance.

- Cost Reduction
Tokenization contributes to cost reduction by automating and streamlining financial processes. Automation minimizes human intervention, leading to fewer errors and a decrease in operational costs. Moreover, the transparency and traceability of blockchain technology reduce the need for costly reconciliation processes associated with traditional banking. For banks, this translates into substantial savings on administrative costs, which can then be passed on to customers in the form of reduced fees or improved service offerings.
- Increased Liquidity
One of the most compelling advantages of tokenization is its ability to transform illiquid assets into tradable tokens. Traditionally, assets like real estate and art are difficult to trade quickly due to high entry barriers and lengthy transaction processes. Tokenization breaks these assets down into smaller, tradable units, effectively democratizing access and increasing market liquidity. For investors, this means easier entry into valuable asset classes with lower capital requirements, while for banks, it opens up new avenues for revenue generation and portfolio diversification.
Challenges and Risks of Tokenization
Despite its advantages, tokenization is not without challenges. Regulatory hurdles present a significant obstacle, as banks must navigate complex legal frameworks to ensure compliance. Technological barriers, such as scalability and integration with existing systems, also pose challenges. Furthermore, consumer trust remains a critical issue, as concerns about privacy and security in digital tokens persist.

Applications of Tokenization in Banking
Tokenization is finding diverse applications within the banking sector. Asset tokenization allows banks to offer tokenized versions of real estate and commodities, providing new investment avenues. In payment systems, tokenization is transforming how transactions are processed, making them more secure and efficient. Additionally, tokenization is enhancing cross-border transactions by reducing costs and improving efficiency in international banking.
The applications of tokenization in banking are vast and varied, each promising to reshape the financial landscape in compelling ways.

- Asset Tokenization
Tokenization is a process of generating tokens digital, which are correlated with physical or hypothetical objects – for example, assets can be the actual property, metals, or ideas that can be protected by law. For example, if there is a piece of property this can be subdivided into many tokens where each token represents a fraction of the property. This makes it possible for there to be more investors in real estate markets without having to acquire the full property, which in turn increases the frequency of transactions and makes real estate more liquid. Also, through the trading of these tokens in the secondary market, banks will act as a marketplace for these tokens opening up the areas of new revenue to their clients.
- Payment Systems
However, in the context of payments, tokenization is disrupting the way that business is transacted. As customers’ payment details are protected by tokens, financial institutions can provide clients with fast, safe, and efficient methods of paying for goods and services. This is well illustrated in contactless payment solutions and digital wallets whereby tokenization lets users be inclined to consume without even disclosing factual account information. Moreover, tokens help to minimize the time needed for the market participants to process transactions and result in faster and more pleasing shopping experiences for customers.
- Cross-Border Transactions
Tokenization is also revolutionizing cross-border transactions, which have always posed a lot of problems such as high costs, fluctuating exchange rates, and long processing duration. Tokenized digital currencies and assets may help the transition to cheaper and quicker cross-border payments for banks. This helps make certain that there is trust between the contracting parties and that the chances of a dispute arising are greatly minimized due to the blockchain’s ability to have an open ledger. This has major consequences for international trade, because firms can, thus, engage in cross-border transactions with more assurance.
Tokenization is rapidly transforming banking services by improving security and by making the ownership of previously illiquid assets more efficient and cost-effective. Therefore, the use of tokenization technology can enhance service delivery in banking sectors and create a suitable ground for future innovation and changes in market demands. As tokenization reaches its pinnacle, the potential of this method will just be unveiled to evolve and bring a new and more liberal platform to all stakeholders in the financial market.
Case Studies of Tokenization in Banking
Several banks have successfully implemented tokenization, offering valuable lessons for the industry. For instance, JPMorgan Chase has developed its digital currency, JPM Coin, to facilitate instant payments between institutional clients. This initiative highlights the potential of tokenization to streamline operations and enhance customer experiences. Early adopters have learned that while challenges exist, the benefits of tokenization far outweigh the risks, paving the way for broader adoption.

Successful Implementations
| Bank | Implementation | Description | Impact and Insights |
| JPMorgan Chase | JPM Coin | A digital token representing fiat currency for instantaneous payments between institutional clients. | Demonstrates the efficiency of blockchain in reducing transaction times and costs in banking. |
| Santander | One Pay FX | A service offering same-day international money transfers through an app, reducing transaction times. | Highlights the benefits of tokenization in enhancing customer experience and transparency in transactions. |
| Deutsche Bank | Project Ubin | A collaborative initiative to experiment with digital payments and securities settlement using blockchain. | Showcases the potential for streamlined cross-border transactions and the importance of collaboration in innovation. |
- JPMorgan Chase: JPM Coin
JPMorgan Chase stands as a beacon of innovation in the banking sector with the development of the JPM Coin. Launched as a digital token representing fiat currency, JPM Coin is used to facilitate instantaneous payments between institutional clients. This tokenized currency operates on a blockchain platform, reducing the time and cost associated with traditional wire transfers. By transforming how funds are moved and settled, JPMorgan has showcased the efficiency and security benefits of tokenization in commercial banking.
- Santander: One Pay FX
Santander’s One Pay FX is another exemplary case of tokenization in action. As one of the first international banks to embrace blockchain for payment processes, Santander utilizes tokenization to offer same-day, international money transfers through its app. This service reduces transaction times from days to minutes, enhances transparency, and cuts costs. Through these improvements, Santander provides an enhanced customer experience, illustrating the direct consumer benefits of tokenization.
- Deutsche Bank: Project Ubin
Deutsche Bank participated in Project Ubin, a collaborative initiative with the Monetary Authority of Singapore and other banks, to experiment with digital payments and securities settlement using blockchain technology. The project demonstrated the viability of a unified platform for tokenized assets and currencies, highlighting how tokenization can streamline cross-border transactions and settlements. This collaborative effort has paved the way for further innovations in digital banking and cross-border functionality.
Lessons Learned

- Navigating Regulatory Landscapes
One of the critical lessons from early implementations is the importance of understanding and aligning with regulatory requirements. Banks like JPMorgan and Santander faced challenges with compliance and legal frameworks, necessitating close collaboration with regulators. These banks learned that proactive engagement and transparent dialogue with regulatory bodies are essential for overcoming hurdles and facilitating the smoother implementation of tokenization technologies.
- Technology Integration and Scalability
Another lesson centers around the technological challenges of integrating tokenization into existing systems. Banks discovered that while blockchain offers numerous benefits, issues such as scalability and interoperability with legacy systems can impede progress. For successful integration, banks need to invest in upgrading their technological infrastructure and fostering an environment that supports innovation and flexibility.
- Building Customer Trust
Customer trust emerged as a pivotal factor for successful adoption. Early cases like Santander’s One Pay FX highlighted that transparency, security, and ease of use are crucial for gaining customer confidence in tokenized services. By focusing on enhancing user experience and communicating the safety and benefits of tokenization, banks can foster greater acceptance among their clientele.
- Strategic Partnerships
Partnerships with technology providers and other financial institutions are instrumental in the successful deployment of tokenization solutions. Collaborative efforts, such as those demonstrated in Project Ubin, leverage shared expertise and resources, leading to more robust and innovative implementations. Banks have learned that building a network of strategic partnerships can accelerate the adoption and effectiveness of tokenization projects.

Future Trends in Tokenization
The future of tokenization in banking is closely tied to the integration of blockchain technology. As blockchain becomes more prevalent, tokenization will play an increasingly vital role in advancing financial services. Experts predict that tokenization will continue to evolve, offering new opportunities for banks to innovate and improve their offerings.
Tokenova’s Role in Tokenization
Tokenova is at the forefront of supporting banks in their tokenization efforts. By offering comprehensive services, Tokenova helps financial institutions navigate the complexities of tokenization, from compliance and security to smart contract deployment. Their expertise enables banks to implement tokenization solutions effectively, ensuring a smooth transition to digital asset management.
Conclusion
In conclusion, tokenization is transforming the banking sector by enhancing security, efficiency, and liquidity. As we look to the future, the potential for tokenization to revolutionize finance is immense, offering exciting opportunities for banks and investors alike. By embracing this technology, the banking industry can unlock new levels of innovation and growth.
How does tokenization differ from traditional encryption?
Tokenization replaces sensitive data with a token, while encryption scrambles data into a code. Tokens are stored separately from the original data, enhancing security.
Can tokenization be applied to all types of assets?
While tokenization is versatile, its application depends on regulatory frameworks and the nature of the asset. Some assets may face more challenges in tokenization than others.
What role does blockchain play in tokenization?
Blockchain provides the decentralized and secure infrastructure necessary for tokenization, ensuring transparency and immutability in transactions.
How does tokenization impact customer experience in banking?
Tokenization enhances customer experience by providing faster, more secure transactions and enabling access to a broader range of financial products.
What are the environmental impacts of tokenization in banking?
While blockchain technology can be energy-intensive, efforts are underway to develop more sustainable solutions, reducing the environmental footprint of tokenization.