In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, blockchain governance has emerged as a pivotal component shaping innovation, trust, and efficiency across sectors. As the global blockchain market surges toward a projected \$1000 billion by 2032, understanding how governance influences smart contract functionality becomes increasingly critical.
At the heart of this evolution are smart contracts—self-executing digital agreements with terms encoded directly into software. These tools streamline operations, reduce human error, and ensure tamper-proof execution within governed blockchain ecosystems.
For entrepreneurs, tech pioneers, and modern businesses striving for operational excellence, understanding the types of smart contracts in blockchain governance is essential. This guide explores ten key contract types, unveiling their features, real-world applications, and how governance frameworks enhance their security, transparency, and adaptability.
By the end of this Tokenova journey, you’ll discover how smart contracts, under effective blockchain governance, can transform your operations, slash costs, and drive next-level innovation.
Introduction to Smart Contracts in Blockchain
Before we explore specific types, it’s vital to understand what smart contracts are and why they’re central to blockchain governance. Their origin and key features help clarify their role in enhancing decentralized decision-making and operational efficiency.

What Are Smart Contracts?
Smart contracts are digital protocols that automatically execute and enforce agreements when predefined conditions are met. Built on blockchain’s decentralized architecture, they offer transparency, security, and immutability—key pillars of effective blockchain governance. By removing intermediaries, they enable faster, more reliable, and less error-prone transactions.
A Brief History of Smart Contracts
The concept of smart contracts was introduced by Nick Szabo in the 1990s, but it gained real traction with the rise of blockchain platforms like Ethereum. These platforms provided the ideal infrastructure for self-executing agreements, allowing developers to create decentralized applications (dApps) aligned with the principles of transparent and autonomous governance.
The Importance of Smart Contracts
Smart contracts automate complex business processes and reduce dependence on centralized authorities, aligning perfectly with the goals of blockchain governance. They reduce costs, boost trust, and ensure all parties operate with the same tamper-proof data—building reliable and transparent ecosystems.
Key Features of Smart Contracts
To truly appreciate the versatility and transformative potential of smart contracts across various industries, it’s crucial to understand their fundamental characteristics. These features are what set them apart from traditional contracts and enable their unique capabilities.

Distributed Nature
Smart contracts are replicated across nodes in the blockchain, ensuring decentralization, reliability, and shared access. This structure eliminates single points of failure and upholds the governance principle of decentralization, where no single entity has unilateral control—making systems more resilient and trustworthy.
Immutable Agreements
Once a smart contract is deployed onto the blockchain, it becomes virtually tamper-proof and unchangeable. This immutability is a critical feature, guaranteeing that the agreed-upon terms remain constant and inviolable throughout the contract’s lifecycle. This provides unparalleled assurance to all parties involved, effectively preventing any unauthorized modifications or retrospective alterations. Any attempt to tamper with the contract would be immediately rejected by the network’s consensus mechanism, thereby safeguarding the integrity and dependability of the agreement. Immutability is a core principle that builds confidence in smart contracts.
Self-Executing Code
A defining characteristic of smart contracts is their ability to self-execute automatically when predefined conditions are verifiably met. This self-execution mechanism eliminates the need for manual intervention at the point of execution, significantly reducing delays and the potential for human error. The automation ensures that actions are performed consistently and with precision, strictly adhering to the contract’s terms without any deviation or subjective interpretation. This feature is central to the efficiency and reliability offered by smart contracts.
Transparent Operations
Transparency is inherent in smart contracts. Every participant with permission can readily view the complete code and terms of the smart contract directly on the blockchain. This radical transparency ensures that all terms are unequivocally clear and easily accessible, fostering a high degree of trust among all involved parties. This open nature of smart contracts also greatly simplifies auditing and compliance processes, as all transactions and contract conditions are publicly recorded and immutably stored on the blockchain. Transparency builds confidence and facilitates accountability in smart contract applications.
Exploring the Different Types of Smart Contracts in Blockchain
Smart contracts are not monolithic; they come in a variety of specialized forms, each meticulously designed to cater to specific applications and industry needs. Below, we delve into ten primary types of smart contracts in blockchain, highlighting their distinct features, typical applications, and illustrating their utility with real-world examples.
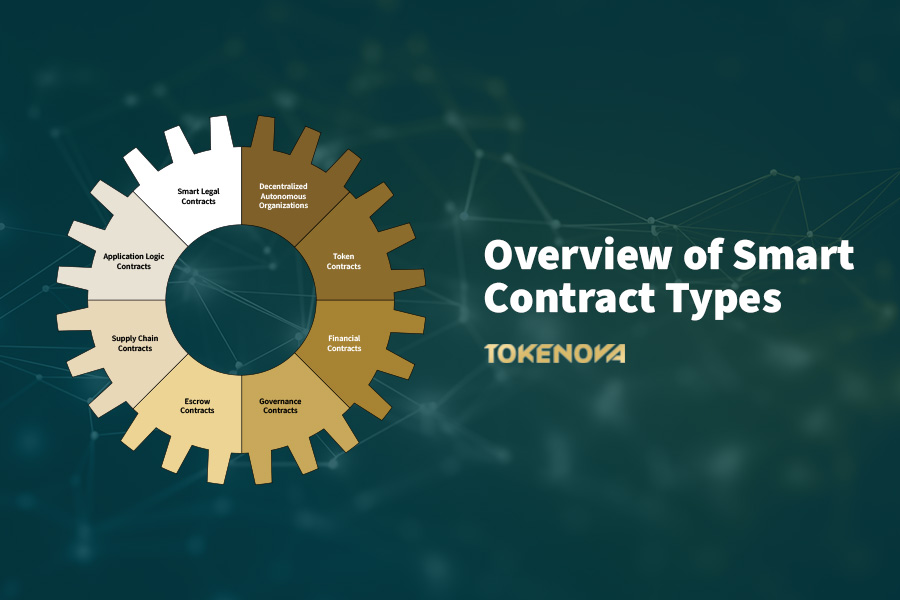
1. Smart Legal Contracts
Smart Legal Contracts merge traditional legal frameworks with blockchain technology, creating legally enforceable agreements that are both transparent and automated. In 2023, approximately 13% of real estate firms reported (statista) using smart contracts, indicating a growing trend in the adoption of legally binding digital agreements. They are legally enforceable agreements that are embedded with digital signatures and executed on a blockchain. These contracts are meticulously designed to be recognized and upheld within existing legal systems, effectively bridging the gap between the digital and legal realms.
Definition and Features
These contracts are not just lines of code; they are legally sound agreements written in code. They incorporate digital signatures to ensure authenticity and non-repudiation, mirroring the legal validity of traditional paper-based contracts. The key feature is their enforceability within legal jurisdictions, making them suitable for scenarios requiring legal compliance.
Applications
- Real Estate: Automating and securing property transfers, ensuring seamless and legally recognized ownership changes as soon as payment is verified.
- Finance: Streamlining and automating loan approvals by automatically disbursing funds when predefined conditions, such as credit checks and collateral verification, are successfully met.
- Legal Services: Revolutionizing legal service delivery by facilitating automated contract execution and efficient dispute resolution mechanisms, reducing reliance on intermediaries.
Consider a real estate firm utilizing Smart Legal Contracts to automate property sales. Once a buyer’s payment is confirmed and digitally signed, the smart contract automatically executes the property transfer, updating the blockchain record to reflect the new ownership. This entire process is legally binding, reduces the need for extensive paperwork and intermediaries, significantly accelerates transaction times, and minimizes the risk of fraudulent activities. This is a powerful use of smart contracts in blockchain for real estate.
2. Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs)
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) represent a revolutionary model for organizational governance. DAOs are essentially organizations that are governed entirely by rules encoded in smart contracts, enabling collective and transparent decision-making processes without any centralized authority. They operate based on predefined rules that are immutably programmed into smart contracts, ensuring democratic governance and fully transparent operations.
Definition and Features
DAOs are organizations run by code. The rules of governance, membership, and operation are all defined in smart contracts. Decisions are made through voting by token holders, and actions are automatically executed by the smart contracts based on these votes. This ensures transparency and eliminates the need for hierarchical management.
Applications
- Investment Funds: Managing decentralized investment pools where investment decisions are made collectively by token holders through transparent voting mechanisms.
- Community Projects: Facilitating collaborative community initiatives where members democratically vote on project directions, resource allocation, and key operational decisions.
Imagine a DAO managing a decentralized investment fund. All members holding governance tokens can propose and vote on potential investment opportunities. The smart contracts automatically execute investments that receive majority approval from the token holders, ensuring transparent and democratic management of the fund. This structure democratizes investment decisions, empowering participants to have a direct say in how their collective funds are allocated and managed. This showcases the advantages of smart contracts in blockchain for governance.
3. Application Logic Contracts (ALCs)
Application Logic Contracts (ALCs) automate interactions between IoT devices by encoding rules into smart contracts. These contracts allow devices to react to real-time data autonomously, without human involvement—aligning with decentralized governance models where systems act independently based on predefined logic.
Definition and Features
ALCs are the backbone of automated device interactions. They define the logic for how devices communicate and react to data. These contracts are crucial for IoT applications, enabling devices to make decisions and trigger actions based on sensor data and predefined rules, all without human oversight.
Applications
- Smart Homes: Automating various home systems such as lighting, heating, and security based on real-time occupancy and environmental conditions detected by sensors.
- Industrial Automation: Managing and optimizing machinery operations in manufacturing environments based on real-time data inputs and predefined operational protocols, enhancing efficiency and reducing downtime.
In a smart home governed by Application Logic Contracts (ALCs), sensors detect occupancy in real time. Based on this input, the smart contract—operating within a blockchain governance framework—automatically turns on lights and adjusts the thermostat for comfort. This decentralized automation enhances energy efficiency and user convenience without manual input, demonstrating a real-world use of smart contracts in IoT systems aligned with autonomous, rule-based governance.
4. Token Contracts
Token Contracts are essential for managing digital tokens on the blockchain. They oversee a token’s entire lifecycle—from creation to transfer—by defining rules for supply, ownership, and transferability. Within the framework of Blockchain Governance, these contracts ensure transparent and consistent token behavior, supporting secure and rule-based digital asset ecosystems.
Definition and Features
Token Contracts are the blueprint for digital tokens. They define the token’s properties, such as its name, symbol, total supply, and divisibility. They also manage the rules for token transfers, burning, and minting. These contracts are essential for creating cryptocurrencies and NFTs.
Applications
- Cryptocurrencies: Creating and managing digital currencies, such as ERC-20 tokens on the Ethereum blockchain, which are widely used for various applications within the crypto ecosystem.
- Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs): Facilitating the creation, issuance, and secure trading of unique digital assets like digital art, collectibles, virtual real estate, and in-game items, each verifiably unique and owned by the holder.
An artist issues NFTs for digital artwork using Token Contracts, with each token representing a unique piece. Through blockchain-based smart contracts and governed rules, buyers can trade NFTs, verify ownership, and ensure authenticity. This system, built on Blockchain Governance, enables transparent, secure, and verifiable transactions—empowering artists and collectors in the digital asset space.
Read More: Exploring the 10 Types of Smart Contracts in Blockchain
5. Supply Chain Contracts
Supply Chain Contracts are designed to revolutionize supply chain management by automating the tracking and verification of goods as they move through the entire supply chain network. They enhance transparency, significantly reduce the incidence of fraud, and boost overall efficiency by providing real-time, end-to-end visibility into the movement, condition, and provenance of products.
Definition and Features
These contracts bring transparency and efficiency to supply chains. They track goods from origin to consumer, recording each step on the blockchain. This includes information like location, temperature, handling conditions, and custody changes. This real-time tracking reduces fraud and improves accountability.
Applications
- Logistics: Real-time monitoring of goods shipments, ensuring timely deliveries, verifying the authenticity of products at each stage, and providing precise location tracking throughout the journey.
- Manufacturing: Tracking raw materials from suppliers to production facilities, ensuring quality control, verifying ethical sourcing, and maintaining compliance with regulatory standards throughout the manufacturing process.
A Supply Chain Contract tracks goods from manufacturer to retailer, automatically recording location, condition, and custody at each stage. Enabled by smart contracts and governed under Blockchain Governance principles, this real-time tracking improves transparency, reduces counterfeit risks, and ensures that all stakeholders access accurate, tamper-proof product data throughout the supply chain.
6. Financial Contracts
Financial Contracts are designed to automate a wide array of financial transactions, encompassing payments, loans, insurance claims, and investments. They are engineered to enhance efficiency, substantially reduce operational costs, and minimize the risk of errors inherent in manual financial operations. These contracts are integral to the rapidly expanding field of Decentralized Finance (DeFi), which aims to create more accessible, transparent, and efficient financial systems that operate outside of traditional financial institutions.
Definition and Features
These contracts automate financial operations. They can handle payments, loans, derivatives, and insurance. By encoding financial agreements into smart contracts, intermediaries are removed, processes are streamlined, and transactions become more transparent and efficient.
Applications
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Enabling peer-to-peer lending and borrowing platforms, facilitating decentralized trading exchanges, and providing access to various financial instruments without traditional intermediaries.
- Insurance: Automating insurance claim processing and payouts based on predefined conditions, such as weather data for crop insurance or flight delays for travel insurance, leading to faster and more transparent claim settlements.
A DeFi platform uses Financial Contracts to let users lend crypto and earn interest. Smart contracts automate loan terms, interest calculations, and repayments—eliminating traditional intermediaries. Within a Blockchain Governance framework, this approach enhances efficiency, broadens access to financial services, and reflects the shift toward decentralized, tokenized banking models.
Read More: Exploring the 10 Types of Smart Contracts in Blockchain
7. Escrow Contracts
Escrow Contracts improve security and trust by holding funds or assets in a neutral digital escrow until all predefined conditions are met. Governed by Blockchain Governance, these smart contracts ensure both parties fulfill obligations before asset release, protecting participants and enhancing transactional trust.
Definition and Features
Escrow Contracts act as neutral intermediaries. They hold funds or assets securely until all parties fulfill their obligations. Once conditions are met (e.g., service delivered, goods received), the contract automatically releases the funds. This reduces the risk of fraud and ensures fair transactions.
Applications
- Freelancing Platforms: Securely releasing payments to freelancers upon successful completion and client approval of the project deliverables, ensuring fair compensation for work done.
- E-commerce Marketplaces: Holding buyer payments securely until the purchased goods are successfully delivered and verified by the buyer, protecting both buyers and sellers in online transactions.
In a freelance marketplace, Escrow Contracts securely hold client payments until project completion and approval. Governed by Blockchain Governance, the smart contract ensures automatic release of funds only when both parties fulfill their obligations, protecting freelancers and clients alike and enabling secure, trustless transactions.
8. Governance Contracts
Governance Contracts enable transparent, democratic decision-making in decentralized systems by encoding voting rules and procedures into smart contracts. Under the principles of Blockchain Governance, these contracts ensure accurate vote tallying, transparent record-keeping, and precise execution of decisions according to predefined governance protocols.
Definition and Features
Governance Contracts automate and secure voting processes. They define voting rules, quorum requirements, and decision-making mechanisms. Token holders can vote on proposals, and the smart contract automatically tallies votes and executes outcomes based on the defined governance rules, ensuring transparency and fairness.
Applications
- Blockchain Network Upgrades: Managing community voting on proposed protocol upgrades and significant changes to the blockchain network itself, ensuring community consensus.
- DAOs Decision-Making: Facilitating decisions within Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) regarding project directions, resource allocation, and strategic initiatives based on member votes.
A blockchain network uses Governance Contracts to enable token holders to vote on protocol changes. The smart contract tallies votes and enforces approved upgrades once consensus is reached. This Blockchain Governance model ensures transparent, tamper-proof, and community-driven decision-making, highlighting smart contracts’ advantages in governance.
9. Identity Verification Contracts
Identity Verification Contracts securely manage and verify digital identities on the blockchain. Within the framework of Blockchain Governance, they enhance security, privacy, and efficiency, playing a crucial role in sectors like finance, healthcare, and government that demand strict identity verification.
Definition and Features
These contracts streamline and secure identity verification. They can manage digital identities, verify credentials, and control access to services based on verified identities. Using blockchain, they enhance security and privacy compared to traditional identity management systems.
Applications
- KYC (Know Your Customer) Compliance: Streamlining and automating customer verification processes in financial services to comply with KYC regulations, reducing manual processes and improving security.
- Secure Access Control: Managing digital identities for secure access to sensitive systems, data, and services, ensuring that only verified and authorized individuals can gain entry.
A financial institution implements Identity Verification Contracts to automate its KYC process. New customers submit their identification documents, which are securely verified and their verified identity is recorded on the blockchain through a smart contract. The smart contract ensures that only individuals with verified identities can access certain financial services, enhancing security and regulatory compliance while simplifying the onboarding process for legitimate customers. This is a crucial use of smart contracts in blockchain for security and compliance.
10. Gaming Contracts
Gaming Contracts revolutionize the gaming industry by enabling true ownership of in-game assets and secure transactions on the blockchain. Governed by Blockchain Governance principles, these contracts grant players verifiable, immutable control over their virtual items, enhancing trust and enabling confident trading, buying, and earning.
Definition and Features
Gaming Contracts revolutionize in-game economies. They enable players to truly own in-game assets as NFTs. These contracts manage the creation, ownership, and trading of virtual items, providing transparency and security to in-game transactions and economies.
Applications
- Virtual Economies: Managing the creation, distribution, and secure trading of in-game assets such as weapons, character skins, virtual land, and other collectibles within virtual worlds.
- Player-Owned Games: Empowering players with ownership and control over game assets and even aspects of the game economy itself, fostering more engaging and player-centric gaming experiences.
In blockchain games, Gaming Contracts represent in-game items as unique NFTs owned verifiably by players. Governed by Blockchain Governance, these smart contracts enable secure trading, selling, and usage of virtual assets, fostering vibrant virtual economies and highlighting smart contracts’ advantages in gaming.
Read More: Exploring the 10 Types of Smart Contracts in Blockchain
How Smart Contracts Work: A Step-by-Step Overview
To fully grasp the transformative power and broad potential of smart contracts, it’s essential to understand their operational workflow. Let’s break down the typical steps involved in creating, deploying, and executing a smart contract.

Step-by-Step Process
- Agreement Phase: The process begins with parties involved reaching a mutual agreement on the specific terms and conditions of their contract. This is similar to traditional contract negotiation, but the outcome will be translated into code.
- Contract Creation (Coding): Once the terms are agreed upon, they are meticulously translated into programming code. Developers write the smart contract, encoding the agreed-upon terms and conditions into a set of executable instructions.
- Deployment to Blockchain: The newly written smart contract is then deployed onto a blockchain network. Upon deployment, it becomes an immutable and publicly accessible part of the blockchain, ready to be executed when conditions are met.
- Condition Monitoring: The blockchain network continuously monitors for the specific conditions defined within the smart contract. This monitoring is automated and decentralized, ensuring accuracy and reliability.
- Automated Execution: As soon as the predefined conditions are verifiably met, the smart contract automatically self-executes. This means the code triggers the agreed-upon actions without any need for manual intervention.
- Transaction Recording: Finally, the execution of the smart contract and its resulting outcome are permanently recorded on the blockchain. This record is transparent, immutable, and auditable, providing a clear and verifiable history of the contract’s execution.
Role of Blockchain in Smart Contracts
Blockchain is more than just a platform—it is the foundation of smart contracts. With its decentralized architecture and consensus mechanisms, Blockchain Governance ensures secure execution, immutable records, and transparent validation of smart contracts. This governance-driven infrastructure upholds trust, integrity, and reliability across all contract interactions.
Read More: Exploring the 10 Types of Smart Contracts in Blockchain
Advantages of Smart Contracts in Blockchain: Key Benefits
The integration of smart contracts with blockchain technology offers a multitude of compelling advantages of smart contracts in blockchain that are transforming traditional processes and creating new opportunities across industries.
Enhanced Efficiency
Smart contracts automate contract execution, eliminating the need for manual oversight and paperwork. This leads to faster transactions and improved workflows.
Increased Transparency
Transparency is a core advantage of smart contracts in blockchain. All parties involved in a smart contract can readily view the contract terms and transaction history on the blockchain. This shared visibility ensures that everyone has access to the same information, fostering trust and reducing the likelihood of disputes arising from misunderstandings or hidden clauses. In industries like supply chain and finance, this transparency ensures that all stakeholders are well-informed and aligned, promoting a more collaborative and trustworthy environment.
Significant Cost Savings
By removing intermediaries like lawyers and brokers, smart contracts lower transaction costs. This efficiency under Blockchain Governance makes agreements more accessible, especially for startups and SMBs, enabling better resource allocation and improved competitiveness.
Robust Security
Security is a paramount advantage of smart contracts in blockchain. Smart contracts are secured by the robust cryptographic encryption and decentralized nature of blockchain technology. Once a smart contract is deployed, it becomes immutable, meaning it cannot be altered or tampered with by any single party. This immutability prevents unauthorized modifications and ensures the integrity of the contract throughout its lifecycle. This high level of security is especially crucial for industries dealing with sensitive data and high-value transactions, such as finance, healthcare, and intellectual property management.
Challenges and Limitations of Smart Contracts
Despite their numerous advantages of smart contracts in blockchain, it’s important to acknowledge that smart contracts also face certain challenges and limitations that need to be addressed for their widespread and effective adoption.
Inherent Rigidity
A major challenge in Blockchain Governance is the immutability of smart contracts. While this feature enhances security, it limits flexibility—making post-deployment changes nearly impossible. Developers must therefore anticipate future needs and embed upgradability mechanisms from the outset.
Read More: Exploring the 10 Types of Smart Contracts in Blockchain
Evolving Legal and Regulatory Landscape
In the context of Blockchain Governance, the evolving legal status of smart contracts poses challenges. With inconsistent regulations across jurisdictions, legal uncertainty can hinder adoption—especially for cross-border applications. Businesses must tread carefully and seek legal guidance to ensure contract validity and compliance.
Scalability Concerns
Scalability remains a significant challenge for some blockchain networks that host smart contracts. Certain blockchain platforms may struggle to handle a high volume of transactions simultaneously, which can limit the performance and efficiency of smart contracts, especially during periods of high network traffic. Scalability issues can lead to transaction delays and increased transaction costs, potentially hindering the widespread adoption of smart contracts for applications requiring high throughput. Ongoing advancements in blockchain technology are actively addressing and scalability issues, but it remains a critical consideration for widespread smart contract adoption.
Future Trends Shaping the Evolution of Smart Contracts
The trajectory of smart contracts is incredibly promising, with continuous advancements and expanding adoption across diverse sectors. Several key trends are poised to shape the future of smart contracts and amplify their impact on industries worldwide.

Synergistic Integration with AI and IoT
A significant trend is the integration of smart contracts with Artificial Intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT), enhancing automation and enabling more dynamic, data-driven agreements. The global smart contracts market size was valued at $684.3 million in 2022 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 82.2% from 2023 to 2030, underscoring the rapid advancement and adoption of this technology. Combining these technologies will pave the way for the development of more sophisticated and truly autonomous systems. This synergy will significantly enhance automation capabilities, enabling smart contracts to become even more dynamic and responsive to real-world data. This integration will unlock new application areas, such as predictive maintenance in manufacturing, intelligent and adaptive supply chain management, and highly personalized customer experiences driven by real-time data analysis.
Accelerated Adoption Across Diverse Industries
Under the lens of Blockchain Governance, the adoption of smart contracts is expected to accelerate across diverse industries—such as healthcare, finance, supply chains, and government services. These sectors are drawn to the operational efficiency, transparency, and cost-saving benefits that smart contracts bring, reinforcing the role of blockchain governance in driving innovation and global economic growth.
Read More: Exploring the 10 Types of Smart Contracts in Blockchain
Development of Enhanced Blockchain Platforms
Ongoing advancements in blockchain technology are crucial for addressing current challenges related to the security and scalability of smart contracts. The development of new and improved blockchain platforms is focused on offering enhanced capabilities, making smart contracts more reliable, efficient, and scalable. These next-generation platforms will likely incorporate features such as improved consensus mechanisms, sharding solutions, and layer-2 scaling technologies. These improvements will facilitate the development and deployment of more complex and high-performance smart contracts, significantly expanding their applicability and utility across various industries and use cases.
Expert Insights: Leveraging Smart Contracts for Business Success

Maximizing the benefits of smart contracts requires not only strategic planning but also informed execution. Here are some expert tips to help you effectively leverage smart contracts for tangible business success:
- Start with Pilot Projects
Under the framework of Blockchain Governance, initiating pilot projects enables organizations to evaluate smart contract effectiveness in a controlled setting, refine strategies, and manage risks before scaling. - Invest in Team Education
Empowering teams with foundational knowledge of smart contracts ensures better alignment with governance protocols and enhances internal capacity to manage and innovate within blockchain systems. - Strategic Collaboration with Experts
Collaborate with blockchain and legal experts to design smart contracts that are secure, compliant, and aligned with governance standards, ensuring both operational integrity and regulatory soundness. - Stay Updated on Industry Developments
Effective blockchain governance requires continuous awareness of evolving technologies, standards, and best practices—enabling agile adaptation and maintaining a forward-thinking approach. - Prioritize User Experience
Integrating usability into smart contract design aligns with governance objectives by encouraging adoption, minimizing errors, and optimizing the overall effectiveness of blockchain-based solutions.
Tokenova: Your Premier Blockchain Advisory Partner
Unlock the full potential of blockchain with Tokenova. As your trusted advisory consultant, we provide expert solutions to drive your business forward.
Our Services
- Smart Contract Development
- Custom, secure, and efficient automation
- Blockchain Strategy Consulting
- Seamless integration and optimization
- Security Audits
- Comprehensive vulnerability assessments
- dApp Development
- Scalable and user-friendly decentralized applications
- Training & Support
- Empower your team with blockchain expertise
Why Choose Tokenova?
- Expert Team: Seasoned blockchain professionals
- Tailored Solutions: Customized to your business needs
- Security Focused: Robust protection for your assets
- Client-Centric: Dedicated to your success
Get Started Today
Don’t wait to transform your blockchain vision into reality. Partner with Tokenova now!
Visit us at www.tokenova.co
Conclusion
Smart contracts are a significant advancement in blockchain technology, providing enhanced efficiency, transparency, and security in executing agreements. By gaining a comprehensive understanding of the diverse types of smart contracts in blockchain, businesses and individuals can unlock a wealth of new opportunities, streamline their operations, and drive significant innovation across various industries. From automating complex property transfers in real estate to enabling decentralized autonomous organizations, smart contracts are fundamentally reshaping the way we conduct transactions, manage agreements, and interact with digital systems.
While challenges such as inherent rigidity and the evolving legal landscape exist, the future of smart contracts is undeniably bright. Ongoing technological advancements and increasing industry adoption are paving the way for a more automated, efficient, and trustless digital economy. Embracing smart contracts today positions you at the forefront of technological innovation, ready to capitalize on the transformative potential of blockchain and lead the way in this exciting new era of digital agreements.
Key Takeaways
- Diverse Types: Smart contracts are not monolithic; they encompass various specialized forms, including Smart Legal Contracts, DAOs, ALCs, Token Contracts, Supply Chain Contracts, Financial Contracts, Escrow Contracts, Governance Contracts, Identity Verification Contracts, and Gaming Contracts, each tailored for specific uses of smart contracts in blockchain.
- Key Advantages: Efficiency gains, enhanced transparency, significant cost savings, and robust security are the primary advantages of smart contracts in blockchain, making them a compelling solution for numerous applications.
- Applications Across Industries: From revolutionizing real estate transactions and healthcare data management to transforming supply chain operations and financial services, smart contracts are demonstrably impacting and improving multiple sectors through automation and enhanced security.
- Future Potential: The future of smart contracts is bright, with ongoing integration with AI and IoT, projected increased industry adoption, and continuous advancements in blockchain platforms promising even greater capabilities and wider applicability.
- Strategic Implementation: To effectively leverage smart contracts, strategic implementation is crucial, including thorough needs assessment, careful platform selection, ensuring legal compliance, rigorous security audits, and continuous monitoring and improvement.
Reference:
Smart Contracts in Blockchain Technology: A Critical Review
An Overview of Smart Contract and Use Cases in Blockchain Technology
What Are Smart Contracts on the Blockchain and How Do They Work?
1. How do smart contracts fundamentally differ from traditional contracts?
Smart contracts are digital agreements that are self-executing and automatically enforce the terms directly written into their code. This automation eliminates the need for intermediaries in the execution and enforcement phases. Traditional contracts, in contrast, require manual enforcement and often involve third parties such as lawyers, courts, or banks to oversee and ensure compliance. Smart contracts offer enhanced efficiency, greater transparency, and improved security by leveraging the inherent capabilities of blockchain technology, streamlining processes and reducing reliance on manual interventions.
2. Is it possible to modify smart contracts after they have been deployed to a blockchain?
Once a smart contract is deployed and confirmed on a blockchain, it becomes inherently immutable. This immutability means that the core code and terms of the deployed contract cannot be directly altered or changed. This feature is a cornerstone of smart contract security and ensures that the agreed-upon terms remain unchanged and prevents any unauthorized modifications. However, developers can design upgradable smart contracts from the outset by incorporating proxy patterns or other advanced architectural mechanisms. These patterns allow for future updates to the contract’s logic without altering the original, immutable contract address, providing a degree of flexibility while maintaining the integrity of the core agreement.
3. Which industries stand to gain the most significant benefits from adopting smart contracts?
Numerous industries are poised to benefit substantially from the adoption of smart contracts. Sectors such as finance, real estate, supply chain management, healthcare, and the gaming industry are particularly well-positioned to leverage the advantages of smart contracts in blockchain. Smart contracts can drive significant improvements in efficiency, reduce operational costs, and enhance transparency across these sectors by automating complex processes and eliminating the need for intermediaries. Furthermore, industries that prioritize secure and transparent transactions, such as insurance, legal services, and intellectual property management, can also effectively utilize smart contracts to streamline operations, build trust, and enhance overall service delivery.