Many crypto investors often face a steep learning curve when entering the world of blockchain. The technical jargon, complex setups, and fear of losing control over assets can make the idea of staking seem risky and confusing.
This uncertainty discourages many from exploring a way to earn passive income through crypto. Without clear guidance on what staking is or what is meant by staking in crypto, potential stakers may feel overwhelmed by the hidden risks and technical details.
A staking platform offers a straightforward solution by simplifying the process of earning rewards. By letting you stake your tokens with ease and security, these platforms remove much of the complexity and provide a clear path into the world of crypto-based passive income.
In this article, you’ll learn:
- How staking platforms simplify the process of earning rewards.
- The key components of staking, including validator selection, rewards, and delegation.
- The benefits and risks associated with different staking platforms.
- Future trends shaping staking platforms in the evolving crypto landscape.
This clear and accessible overview is designed to help you confidently navigate the world of crypto staking, even if you have limited technical knowledge.
Exploring Different Staking Platforms
When it comes to what is staking in crypto, the options are as varied as the investors themselves. Let’s break down the main types of staking platforms in a conversational, easy-to-understand style, and see how each one meets different needs.

Exchange-Based Staking Platforms
Many investors start their journey with exchange-based platforms. These are often part of larger cryptocurrency exchanges like Coinbase, Kraken, and Binance. They integrate staking services directly into their trading platforms, making it incredibly convenient for users who already trade on these exchanges.
Read More: How to Build a Crypto Exchange: The Ultimate 2025 Blueprint for Success
User-Friendly Experience
These platforms provide a seamless experience. For example, on Coinbase, staking is as easy as clicking a button to start earning rewards on Ethereum, Cardano, or Solana—perfect for those who wonder what is meant by staking without diving too deep into the technical details.
Variety of Assets and Reward Tracking
They support multiple cryptocurrencies with varying annual percentage yields (APYs), often offering staking rewards of up to 33%. You can easily monitor your rewards through clear dashboards that show you how much you’re earning.
Considerations
However, most exchange-based platforms are custodial. This means the exchange holds your tokens during the staking period, which can pose risks like hacks or platform insolvency. Understanding these risks is crucial when deciding what is staking in crypto and if the ease of use outweighs potential downsides.
Dedicated Staking Platforms
For those who want more control and advanced features, dedicated staking platforms offer a compelling alternative. Platforms like Staked focus solely on providing staking services, often with more robust options for security and asset management.
Broader Asset Support and Non-Custodial Options
These platforms support a wide range of PoS cryptocurrencies—often more than 45 different assets—giving you a richer variety to choose from. Additionally, many of these services offer non-custodial staking, meaning you retain full control of your private keys, which is a significant benefit if you’re concerned with what is meant by staking in crypto in terms of security and transparency.
Advanced Features for the Serious Investor
Expect 24/7 support, enhanced security protocols, and more refined reward strategies, which can be especially attractive for institutional investors or advanced users. The trade-off is often higher minimum staking requirements and a steeper learning curve compared to exchange-based options.
Decentralized Staking Platforms
For those who enjoy the spirit of decentralization, decentralized staking platforms are an exciting option. These platforms, usually accessible via decentralized applications (dApps) like MetaMask, allow you to stake directly on the blockchain without intermediaries.
Full Control and Transparency
With decentralized platforms, you always know exactly what’s happening with your assets, because you’re interacting directly with the blockchain. This approach answers the question what is meant by staking by putting you in control of your own staking process.
Technical Complexity
However, this approach requires a deeper technical understanding. Setting up and maintaining your own validator node, or simply delegating your stake properly, can involve additional steps that might be daunting for beginners. This type of platform is best suited for those ready to embrace a hands-on approach to what is staking and how does it work.
Staking Pools
Staking pools offer a community-based approach to staking, where groups of token holders come together to pool their resources. This method increases the likelihood of earning rewards, especially in networks with high minimum staking requirements.
Shared Rewards and Lower Barriers
By joining a staking pool, even those with smaller amounts of tokens can benefit from collective staking efforts. Rewards are shared among all pool members based on their individual contributions, making it a practical option for those who ask what is staking in the context of communal investment strategies.
Trust and Risk Management
While pools reduce individual risk, they require you to trust the pool operator. Fees are typically taken from your rewards, and in rare cases, mismanagement can lead to penalties on the pooled stake. As always, it’s important to research the reputation of the pool operator before joining.
Below is a comparison table that outlines the key features of various staking platform types. This table provides a quick overview to help you decide which platform best suits your needs—whether you’re a beginner seeking simplicity, an advanced user looking for control, or someone exploring unique options like staking pools.
| Feature | Exchange-Based Platforms | Dedicated Staking Platforms | Decentralized Platforms | Staking Pools |
| Custodial? | Yes (exchange holds assets) | No (non-custodial options) | No (self-hosted wallets) | Depends (pool operator may hold assets) |
| Asset Variety | 10–30+ cryptocurrencies (e.g., ETH, ADA, SOL) | 45+ PoS coins | Limited to specific chains (e.g., ETH, SOL) | Network-specific (e.g., ADA, DOT) |
| APY Range | 1%–33% (higher for promotional offers) | 3%–15% (varies by asset) | 3%–7% (liquid staking tokens) | 4%–12% (shared rewards after fees) |
| Key Features | – Integrated with trading platforms – Auto-restaking | – Non-custodial control – Institutional-grade tools | – Full transparency – Liquid staking derivatives | – Low minimums – Shared validator responsibilities |
| Risks | Custodial hacks, platform insolvency | Higher minimum deposits, slashing penalties | Smart contract exploits, node operation complexity | Pool operator scams, fee deductions |
| Best For | Beginners seeking simplicity | Advanced users/institutions | Decentralization purists | Smallholders in high-barrier networks |
Diving Deeper: How Does Staking Work?
Understanding what is staking and how it works begins with the Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism—a modern alternative to traditional mining. In PoS, validators are chosen based on the amount of cryptocurrency they stake, making the process both secure and energy efficient. Here’s a breakdown of the process:
Validator Selection
Validator selection is the first step in answering what is staking. This process determines who gets to validate transactions on the network, with your chances tied directly to your staked amount.
Proportional Chance:
Your probability of being chosen is directly proportional to the amount of cryptocurrency you have staked. For example, if you stake 10% of the total tokens, you have roughly a 10% chance of being selected.
Randomized Process:
Despite a higher stake, a random element ensures that even smaller participants can take part. This addresses the common query, what is meant by staking in crypto.
Security Implications:
Validators risk a portion of their staked tokens through “slashing” if they act maliciously, which aligns their interests with maintaining network security.
Rewards and Delegation
This section clarifies what is staking by explaining how rewards are distributed and how delegation works if you’re not running a node.
Earning Rewards:
Validators earn cryptocurrency rewards for processing transactions, directly answering what is staking and how does it work.
Delegation Option:
If operating a node seems too technical, you can delegate your stake to an established validator and still earn rewards. This explains what is meant by staking without the complexities of node operation.
Decentralized Contributions:
Delegation supports network decentralization and enhances security, making it easier for everyone to participate in staking.
Variable Reward Rates
Your rewards from staking can vary, which helps explain what is staking in crypto by highlighting the factors that influence returns.
Read More: Efficiency Gains: Token vs Traditional Investments
Influence of Stake Size:
Larger stakes generally yield higher rewards, with returns proportionate to your contribution.
Lock-Up Duration:
Committing your tokens for longer periods can increase rewards, offering a more stable investment model.
Network Activity:
Fluctuating transaction volumes and overall network activity can influence reward rates.
Auto-Staking Features:
Some platforms offer auto-staking, where rewards are automatically reinvested, compounding your returns over time.
The Benefits and Risks of Staking Platforms
Below is an overview of the benefits and risks of staking:
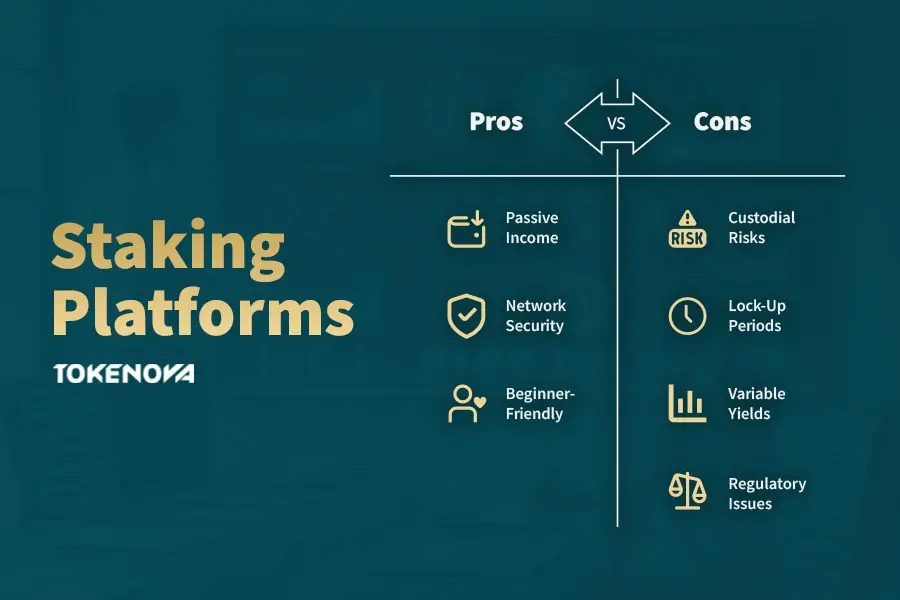
Benefits
Staking platforms offer several advantages that can make participating in crypto both profitable and secure:
Earn Passive Income:
One of the most appealing aspects of staking platforms is the ability to generate a passive income stream. By simply holding and staking your assets, you can earn rewards without having to trade actively.
Support Network Security:
When you stake your tokens, you’re directly contributing to the security and efficiency of blockchain networks. This decentralized participation is crucial for the sustainability of the crypto ecosystem.
Accessibility for Beginners:
Staking platforms lower the barrier to entry. Whether you’re wondering what is a staking platform or what is meant by staking in crypto, these platforms make it easier for anyone to join in—even without deep technical knowledge.
Risks
However, like any investment, staking comes with its own set of risks that you should consider before diving in:
Custodial Risks:
Platforms that hold your tokens for you (custodial staking) might be susceptible to hacks or financial instability. This risk is a key consideration for anyone asking what is staking in crypto and weighing their options.
Lock-Up Periods:
Some staking options require you to lock up your assets for a predetermined period, limiting your liquidity. This can be a drawback if market conditions change suddenly.
Fee Structures and Variable Yields:
Platform fees and fluctuating reward rates can impact your overall returns. High yields may seem enticing, but they could also indicate higher risk levels or unsustainable reward models.
Read More: Top Asset Tokenization Challenges & How to Overcome Them
Regulatory and Tax Considerations:
The regulatory landscape around staking is still evolving. Investors must be aware of potential tax implications and legal requirements in their jurisdiction.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Staking Platforms
Staking platforms are evolving rapidly, driven by technological innovation, regulatory shifts, and growing institutional interest. As blockchain ecosystems mature in 2025, these platforms are expanding their utility beyond passive income to become critical infrastructure for decentralized governance, cross-chain interoperability, and sustainable finance. Here’s a detailed look at the emerging trends and future directions:
- Cross-Chain and Multi-Chain Staking:
Platforms like Babylon and EigenLayer are pioneering the ability to stake assets across multiple blockchains. This innovation not only allows investors to diversify rewards across ecosystems like Ethereum, Solana, and Polkadot but also ensures liquidity even when staking assets such as Bitcoin on PoS networks. - Institutional Adoption:
Financial institutions are increasingly turning to crypto staking as a yield-generating tool in low-interest environments. With platforms such as Keynode and Coinbase offering institutional-grade services, including compliance frameworks and enhanced security. - Liquid Staking Dominance:
Liquid staking protocols like Lido Finance and Rocket Pool are reshaping the market by allowing users to retain liquidity through derivative tokens (e.g., stETH). These tokens can be used in DeFi for lending, collateral, or trading, creating layered yield opportunities while answering the question of what is staking in a modern, versatile context. - Restaking and Yield Innovation:
Innovative platforms like EigenLayer now allow users to “restake” assets—staking already staked tokens across multiple protocols to amplify rewards. Additionally, yield tokenization through platforms like Pendle Finance is converting future staking yields into tradable tokens, enabling risk hedging or speculative strategies. - Eco-Friendly Staking:
With sustainability in focus, platforms such as Avalanche and Polygon prioritize energy-efficient consensus mechanisms and even offset carbon emissions through climate partnerships, attracting ESG-conscious investors. - NFTs and Metaverse Integration:
Staking is expanding into virtual ecosystems. NFT staking is becoming popular for earning rewards or unlocking exclusive content in gaming and metaverse platforms, while staking virtual land or governance tokens (like Decentraland’s MANA) can grant voting rights and revenue shares, bridging the gap between digital assets and virtual economies.
Technological and Regulatory Advancements
Enhanced Security:
New measures, such as slashing insurance provided by platforms like Keynode, are mitigating the risks of validator penalties. Additionally, multi-layered security protocols—combining cold storage, real-time monitoring, and bug bounties—are becoming standard to combat hacking risks.
Read More: Tokenization in Cyber Security
Regulatory Clarity:
As governments introduce frameworks to classify staking rewards and enforce AML/KYC compliance, regulated platforms like Kraken and Coinbase are leading the way. This transparency not only builds trust but also encourages more cautious investors to explore what is staking in crypto.
Read More: Asset Tokenization Regulation
Conclusion
Staking platforms have revolutionized the way cryptocurrency holders engage with the market. They answer the question of what is a staking platform by providing accessible, secure, and efficient methods to earn passive income and support blockchain networks. Whether you’re exploring what is staking as a beginner or diving into the technical nuances of what is staking and how does it work, there’s a solution that fits your needs—be it exchange-based, dedicated, decentralized, or pooled staking.
As the crypto ecosystem continues to evolve, staying informed and doing thorough research will help you make the most of your investments while navigating the risks and rewards of staking platforms.
How does staking impact the decentralization of a blockchain network?
Staking plays a crucial role in decentralization by incentivizing more participants to validate transactions and secure the network. However, centralization risks can arise if a few large validators control a disproportionate share of the staked assets. To mitigate this, some networks implement mechanisms like stake delegation, slashing penalties, and validator rotation to distribute power more evenly.
Can I stake my crypto without locking it up, and what are the trade-offs?
Yes, some platforms offer liquid staking, which allows you to stake your crypto while receiving a tradable derivative token (e.g., stETH for Ethereum). This lets you maintain liquidity and use your assets in DeFi applications while still earning staking rewards. However, liquid staking comes with risks such as smart contract vulnerabilities and price fluctuations of the derivative token relative to the original asset.
How do staking rewards change during market volatility?
Staking rewards are influenced by factors like network transaction volume, validator competition, and inflation models set by the blockchain protocol. During high volatility, networks with dynamic reward structures may adjust APYs based on staked supply and demand. Additionally, if a network experiences sudden price drops, the real value of staking rewards (measured in fiat) may decrease, even if the percentage yield remains the same.