Decentralized Finance (DeFi) lending platforms are revolutionizing access to capital and yield generation. The core mechanism enabling these platforms to operate without traditional financial intermediaries is the ingenious combination of smart contracts and over-collateralization. In essence, most DeFi lending platform mechanisms rely on these two pillars to manage loans securely and efficiently. This article provides a comprehensive exploration of these DeFi loan management mechanisms, explaining precisely how DeFi lending works, why these mechanisms are essential, and how they are shaping the future of finance. By understanding these innovative approaches, users can navigate the world of decentralized lending with greater confidence and insight.
A Brief Intro to DeFi Lending Platforms
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) represents a fundamental shift in financial services. As of early 2025, the total value locked (TVL) across multiple DeFi blockchains reached approximately $120 billion, reflecting rapid adoption and the emergence of innovative protocols. For entrepreneurs, tech innovators, and business leaders, DeFi offers unprecedented opportunities to access funding, generate returns, and pioneer novel financial solutions. A foundational understanding of DeFi, particularly its DeFi loan management mechanisms, is paramount to effectively leveraging this transformative space.

Read More: What Assets Can Be Tokenized?
A 3D isometric illustration showing people interacting with decentralized finance interfaces, sending and receiving digital assets.
What is DeFi Lending?
DeFi lending fundamentally redefines borrowing and lending through blockchain technology. Moving away from centralized financial institutions, DeFi platforms utilize decentralized protocols to establish direct connections between lenders and borrowers. This peer-to-peer or peer-to-protocol model disintermediates traditional finance, potentially delivering enhanced efficiency, greater transparency, and broader accessibility. Envision an open, global financial marketplace, operational 24/7.
Within DeFi, loan processes are streamlined and automated. Users can secure loans or lend assets via self-executing smart contracts, bypassing cumbersome applications and conventional bank approvals. This financial democratization unlocks opportunities for individuals and enterprises previously underserved by traditional systems. Reduced fees and potentially improved yields are frequently additional advantages. This evolution towards a more inclusive and user-centric financial paradigm is powered by sophisticated DeFi loan management mechanisms.
Why Loan Management is Key
Traditional finance relies on institutional trust and legal frameworks, while DeFi builds trust through verifiable code and cryptographic security. This makes reliable DeFi loan mechanisms essential for securing assets, ensuring loan repayment, and maintaining platform stability. Without them, platforms risk defaults, manipulation, and a loss of user confidence, slowing the natural growth of how DeFi lending works.
Effective DeFi loan mechanisms go beyond preventing loss; they foster a trustworthy, resilient ecosystem through transparent, auditable, and robust systems. When users understand and trust these mechanisms, participation and innovation increase, making a solid grasp of them vital for anyone engaging with this transformative financial space.
Core DeFi Loan Mechanisms
What are the essential mechanisms that underpin DeFi lending platform mechanisms and ensure the seamless functioning of decentralized loans? The answer lies in a synergy of advanced technologies and robust economic principles, primarily centered on smart contracts, over-collateralization, and refined interest rate models. These constitute the fundamental pillars of decentralized finance and are key to understanding how DeFi lending works.
Smart Contracts: DeFi’s Automation Engine
Smart contracts are the bedrock of DeFi lending, acting as self-executing agreements with terms encoded directly into software. Like a financial kiosk, they take inputs (collateral, loan request) and automatically deliver outputs (the loan) based on preset rules — capturing the essence of DeFi loan mechanisms.
They automate every phase of the loan lifecycle, from initiation to collateral management and liquidation, removing intermediaries and acting instantly when conditions are met. This boosts efficiency, transparency, and reduces human error, making smart contracts a core pillar of trust and dependability within DeFi loan mechanisms.
Read More: What Assets Can Be Tokenized?
Over-collateralization: The DeFi Safety Net
A defining feature of most DeFi loan mechanisms is over-collateralization. Unlike traditional lending, which relies on creditworthiness, DeFi requires borrowers to deposit collateral worth much more than the loan to manage risk in a decentralized, pseudonymous system. While over-collateralization is crucial for securing loans, new decentralized credit scoring and under-collateralized options, like those from RociFi, are offering more flexibility.
This approach acts as a vital safety net: if a borrower defaults, the platform can liquidate the collateral to cover the loan and interest. With ratios typically between 150% and 200%, even declining collateral values are usually sufficient. Though less capital-efficient for borrowers, over-collateralization is a fundamental risk management strategy, ensuring lender protection and platform stability within DeFi loan mechanisms.
Recent developments in decentralized credit scoring models and under-collateralized loans are beginning to offer borrowers more flexible options. Protocols like RociFi leverage on-chain data and machine learning to assess creditworthiness without sacrificing decentralization. These innovations aim to enhance capital efficiency while maintaining the security and stability that over-collateralization provides
Read More: The Utility Token of a Decentralized Lending Platform
Interest Rate Models: Algorithmic Pricing
Interest rates are central to any lending system, and DeFi is no exception. Unlike traditional finance, DeFi loan mechanisms use algorithmic or dynamic models that adjust rates in real time based on supply and demand, creating a self-regulating borrowing and lending market.
These models maintain platform balance: when borrowing demand is high, rates rise to encourage lending; when demand is low, rates drop to stimulate borrowing. Some DeFi loan mechanisms use simple utilization-based algorithms, while others factor in volatility and risk. Overall, these models ensure efficient, responsive capital pricing in a decentralized environment and are key to how DeFi lending works.
Collateralization in DeFi Lending
Further examination of collateralization underscores its central role in DeFi loan management mechanisms. Understanding the function of collateral, the spectrum of accepted assets, and the significance of Loan-to-Value (LTV) ratios is essential for anyone participating in DeFi lending and seeking to understand how DeFi lending works.
Collateral’s Role in Loan Security
Collateral in DeFi lending, mirroring traditional lending, secures the loan and mitigates risk for the lender. However, in DeFi, collateral assumes an even more critical role due to participant pseudonymity and the absence of conventional legal recourse. Collateral serves as the primary assurance of repayment within sophisticated DeFi loan management mechanisms.

By mandating collateral, DeFi platforms incentivize borrowers to prioritize loan repayment. Defaulting borrowers risk forfeiting their collateral, which is typically valued higher than the borrowed amount. This alignment of lender and borrower interests fosters a more secure and dependable lending environment. Collateralization is not merely about risk mitigation; it is about establishing trust and confidence in a decentralized system lacking traditional trust infrastructures. It is the bedrock of secure and sustainable DeFi lending platform mechanisms.
Types of Collateral Accepted
The array of assets accepted as collateral on DeFi lending platforms is continuously expanding, reflecting the dynamic nature of the cryptocurrency market. Initially, platforms primarily accepted major cryptocurrencies such as Ether (ETH) and Bitcoin (BTC). However, the maturing DeFi ecosystem now accommodates a significantly broader variety of collateral assets within its advanced DeFi loan management mechanisms.
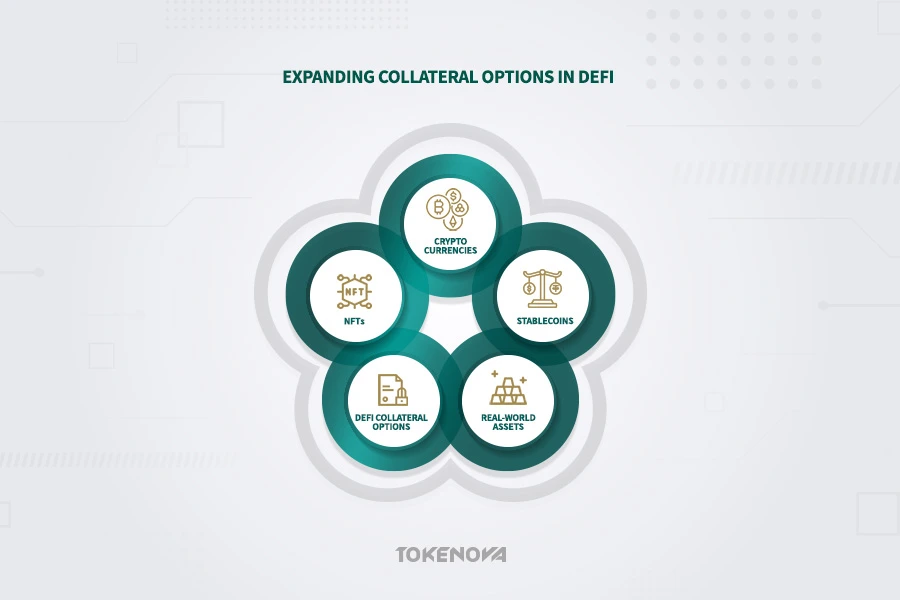
Many platforms now accept a wide range of cryptocurrencies, including stablecoins (USDT, USDC, DAI), and are increasingly exploring tokenized real-world assets (RWAs) and NFTs as collateral, showing the blend of traditional finance and DeFi. For example, integrating on-chain credit scores supports under-collateralized lending, expanding collateral options.
Stablecoins stand out for their lower volatility, while using RWAs helps bridge traditional finance and DeFi. This diversification improves flexibility and broadens access, reflecting the ongoing innovation within robust DeFi loan mechanisms.
Read More: What Assets Can Be Tokenized?
LTV Ratios: Balancing Risk and Efficiency
The Loan-to-Value (LTV) ratio is a key metric in DeFi lending, showing the loan amount relative to the collateral’s value — for example, a 75% LTV lets a borrower get $75 for $100 of collateral. This ratio is crucial for managing risk and ensuring platform stability.
Lower LTV ratios reduce liquidation risk but limit borrowing, while higher LTV ratios increase borrowing capacity but raise the chance of liquidation if collateral drops in value. DeFi platforms must balance LTV settings to appeal to both borrowers and lenders while managing risk.
Different platforms, like Aave (up to 80% LTV) and YouHodler (up to 90% LTV), set varying ratios based on asset volatility and liquidity. For borrowers, understanding LTV ratios helps avoid unexpected liquidations; for lenders, it’s essential for assessing loan risk and making informed decisions.
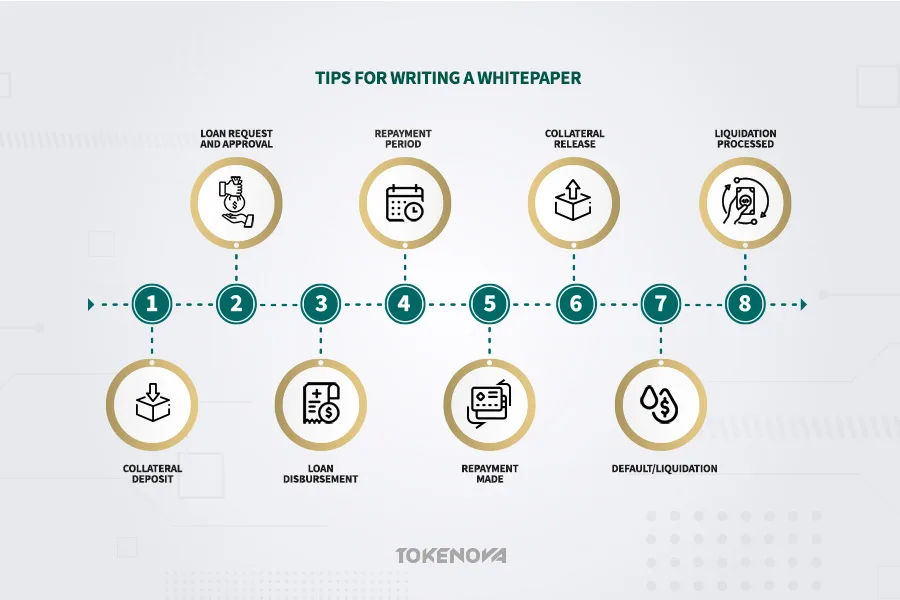
Liquidation Processes in DeFi
Liquidation is a critical, though sometimes misunderstood, aspect of DeFi loan management mechanisms. It is the automated process ensuring platform solvency and protecting lenders when borrowers fail to maintain sufficient collateral. Understanding liquidation processes, their automated nature, and associated risks is vital for anyone involved in DeFi lending and seeking to understand how DeFi lending works.
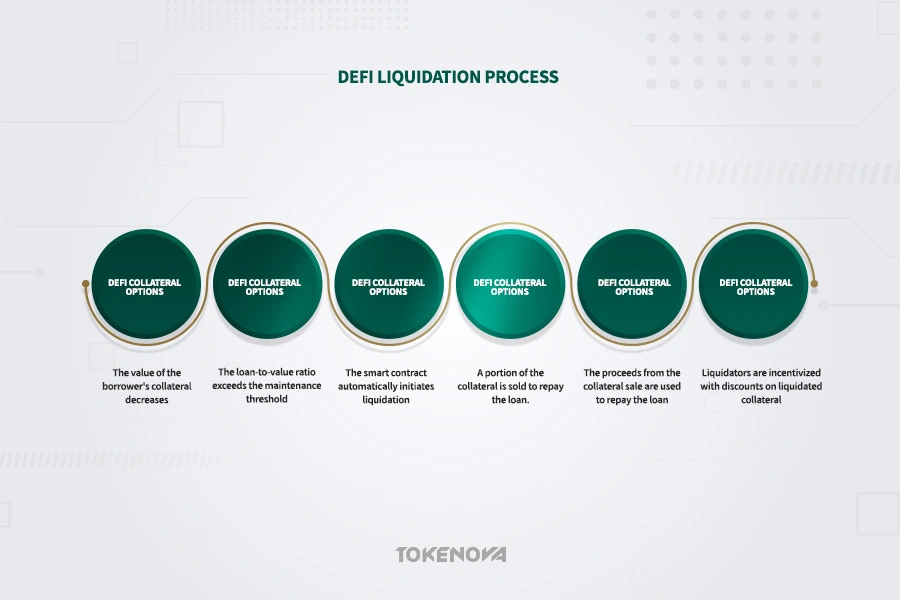
How DeFi Liquidation Works
In DeFi, liquidation is triggered when a borrower’s collateral drops below the set maintenance LTV ratio. If the LTV exceeds this threshold, the smart contract automatically starts liquidation — a core part of DeFi loan management mechanisms.
The process sells part of the borrower’s collateral to cover the loan and interest, with liquidators incentivized by discounts. This ensures fast, efficient liquidations, maintaining platform solvency and protecting lender funds, acting as an automated safeguard to uphold the stability of DeFi lending platforms.
In May 2021, a significant crypto market downturn triggered substantial liquidations across DeFi platforms like Compound and Aave. While these liquidations functioned as intended, protecting lender capital, they also resulted in considerable losses for borrowers who were liquidated. This event underscored both the efficacy and the inherent risks associated with automated liquidation within DeFi loan management mechanisms. It is reported that over $8 billion in liquidations occurred during this crash, highlighting the scale and impact of these automated processes.
Automated Liquidation via Smart Contracts
Automated liquidation via smart contracts is a defining feature of DeFi lending and a key part of DeFi loan management mechanisms. Unlike traditional, slow, and manual liquidation processes, DeFi liquidations are carried out automatically and transparently by code. This automation is essential for the efficiency and reliability of DeFi lending platforms and the smooth functioning of how DeFi lending works.
Smart contracts constantly monitor loan health by tracking collateral values. When a loan becomes under-collateralized, the smart contract triggers liquidation automatically, without manual steps or legal delays. This fast, efficient response is especially critical in the volatile crypto market, where prices can shift quickly. Automated liquidation allows platforms to swiftly adapt to market changes and manage risks effectively, showcasing the strength of smart contracts in building resilient financial systems within advanced DeFi loan management mechanisms.
Read More: What Assets Can Be Tokenized?
Liquidation Risks for Borrowers
While crucial for platform solvency, liquidation carries inherent risks for borrowers in DeFi loan management mechanisms. The main risk is losing collateral during liquidation, especially in volatile markets where sharp price drops can lead to significant losses, directly affecting how DeFi lending works for borrowers.
Additional costs like liquidation penalties or fees can further reduce what’s returned after repayment, and “slippage” — selling collateral at lower-than-expected prices due to market conditions or speed — adds to the risk. To avoid these outcomes, borrowers must carefully monitor their collateralization ratios. A solid understanding of these liquidation details is essential for navigating DeFi platforms responsibly and participating effectively.
Read More: What Assets Can Be Tokenized?
Interest Rates & Yield Generation
Interest rates are the engine that drives DeFi lending, attracting lenders seeking yield and borrowers seeking capital. Understanding interest rate determination in DeFi, the role of yield farming, and the comparison of fixed and variable rates is essential for grasping the dynamics of DeFi loan management mechanisms and fully understanding how DeFi lending works.
Interest Rate Determination in DeFi
DeFi platforms use algorithmic interest rate models that adjust dynamically based on real-time supply and demand, reflecting the current borrowing and lending environment within advanced DeFi loan management mechanisms.
When borrowing demand is high and supply is tight, utilization rises, prompting algorithms to raise interest rates, encouraging more lending and curbing borrowing. When demand is low and supply is plentiful, rates drop, spurring borrowing and lowering lending incentives. This dynamic balance ensures rates stay responsive to market conditions and distinguishes DeFi lending platform mechanisms from traditional finance, fundamentally shaping how DeFi lending works.
Read More: What Can Users Do on Decentralized Lending Platforms?
Yield Farming’s Role in Lending
Yield farming has become a significant phenomenon in DeFi, effectively attracting liquidity to lending platforms and enhancing lender returns. It involves strategically depositing or lending assets on DeFi platforms to earn additional rewards, often in the form of platform-specific tokens or other cryptocurrencies, significantly enhancing the attractiveness of DeFi loan management mechanisms.

Lending platforms frequently incentivize asset deposits by offering yield farming rewards in addition to the interest earned from lending. These rewards can substantially increase lender yields, making DeFi lending a more compelling option compared to traditional savings or fixed-income instruments. Yield farming also bootstraps liquidity for lending platforms, ensuring sufficient capital availability to meet borrowing demand. It is a powerful mechanism fueling the expansion of DeFi loan management mechanisms, creating a positive feedback loop of amplified liquidity, improved yields, and greater user participation, and significantly influencing how DeFi lending works in practice.
Compound Finance’s COMP token distribution in 2020 serves as a prime example of yield farming’s transformative impact. By distributing COMP tokens to users who borrowed or lent assets on the platform, Compound incentivized widespread participation, rapidly expanding its liquidity and user base. This case study vividly demonstrates the effectiveness of yield farming as a robust growth strategy within sophisticated DeFi loan management mechanisms. Messari’s analysis details how Compound’s liquidity mining program spurred significant growth and adoption.
Fixed vs. Variable Interest Rates
DeFi lending platforms typically offer both variable and, increasingly, fixed interest rate options within their comprehensive DeFi loan management mechanisms. Variable interest rates, as previously discussed, fluctuate based on supply and demand dynamics. Fixed interest rates, in contrast, offer a predetermined interest rate for a specified loan term, providing enhanced predictability for both borrowers and lenders, offering diverse approaches to how DeFi lending works.

Variable rates can be advantageous for lenders when borrowing demand is elevated, potentially yielding higher returns. However, they also carry the risk of rates declining if borrowing demand diminishes. Fixed rates offer stability and predictability, appealing to those who prioritize certainty over potentially higher but fluctuating variable rates. The optimal choice depends on individual risk tolerance, market perspectives, and investment objectives. Understanding both options is crucial for effectively utilizing DeFi loan management mechanisms and optimizing returns or minimizing borrowing costs, and for fully grasping the nuances of how DeFi lending works.
Decentralized Governance in Loan Management
Decentralized governance is another defining feature of many DeFi platforms, extending to the critical domain of loan management. DAOs (Decentralized Autonomous Organizations) and community-driven decision-making are increasingly shaping the evolution of DeFi loan management mechanisms and profoundly influencing the long-term trajectory of how DeFi lending works.
DAOs: Governing DeFi Protocols
DAOs are community-governed entities leveraging blockchain technology for decentralized decision-making. In DeFi lending, DAOs often govern protocols, including crucial loan management parameters such as interest rate models, collateral types, LTV ratios, and comprehensive risk management strategies within advanced DeFi loan management mechanisms.

Token holders of a DeFi platform’s governance token typically possess voting rights within the DAO. They can propose and vote on protocol modifications, directly influencing the platform’s strategic direction. This decentralized governance model empowers the community to collectively shape the platform’s future, ensuring alignment with the collective interests of its users. DAOs represent a paradigm shift in how financial protocols are governed, transitioning away from centralized control towards more democratic, community-centric approaches to DeFi loan management mechanisms, fundamentally altering how DeFi lending works and evolves.
Community-Driven Decisions
Community-driven decision-making through DAOs strengthens transparency, inclusivity, and resilience within DeFi lending platforms and their advanced DeFi loan management mechanisms. Unlike centralized authority, collective decisions reduce single points of failure, creating a more robust and adaptable system for how DeFi lending works.
This governance model brings in diverse perspectives and expertise for critical loan management, with blockchain-based, auditable proposals and voting enhancing trust and confidence. While challenges like ensuring broad participation and preventing governance attacks remain, community-driven decision-making remains a powerful force shaping the future of DeFi loan management mechanisms and the broader DeFi ecosystem, greatly influencing how DeFi lending evolves.
Security & Risk Management
Security and risk management are paramount in DeFi lending, given the inherent risks associated with smart contracts, cryptocurrency volatility, and the nascent nature of the technology. Understanding common risks, the role of insurance protocols, and the critical importance of audits and transparency is crucial for navigating the security landscape of DeFi loan management mechanisms and understanding the practicalities of how DeFi lending works safely.
Common DeFi Lending Risks
DeFi lending platforms, though innovative with their advanced DeFi loan management mechanisms, come with inherent risks. A major concern is smart contract vulnerabilities, as these coded agreements can be exploited by malicious actors, and their immutable nature makes fixes difficult and potentially risky, affecting the security of how DeFi lending works.
Impermanent loss is another key risk, especially on platforms using liquidity pools, where price shifts between assets can reduce the value of deposits. Additionally, oracle manipulation—where attackers distort price feeds—can trigger false liquidations or reveal other weaknesses within DeFi mechanisms.
Economic risks like extreme market volatility or cascading liquidations further threaten platform stability and the reliability of DeFi lending. Recognizing these risks is a critical first step toward building stronger, more resilient DeFi lending systems.
In 2024, the DeFi landscape witnessed losses exceeding $2.3 billion across 760 on-chain security incidents due to exploits and hacks, underscoring the persistent security risks within the sector These figures represent an approximate 31.61% increase in value stolen compared to 2023. The number of security incidents year-over-year increased by 29. CertiK’s 2023 Web3 Security Report details these losses, emphasizing the critical need for robust DeFi loan management mechanisms and stringent security protocols.
Read More: What Is the Risk of Lending in Defi Platforms?
Insurance Protocols for DeFi Loans
To mitigate the inherent risks in DeFi loan management mechanisms, insurance protocols are emerging as a vital part of the ecosystem. These protocols provide essential coverage against risks like smart contract vulnerabilities, oracle failures, and stablecoin de-pegging, offering a critical safety net for users engaged in DeFi lending.
Users can purchase insurance for their deposited or borrowed assets, adding protection against unexpected events. Operating in a decentralized way through smart contracts and tokenized policies, these protocols enhance transparency and efficiency. Although still developing, DeFi insurance is rapidly gaining importance for building trust, supporting sustainable growth, and expanding the adoption of DeFi lending.
Audits & Transparency in DeFi
Audits and transparency are essential for building trust and credibility within DeFi lending platforms and their robust DeFi loan management mechanisms. Independent security firms perform detailed smart contract audits to identify potential vulnerabilities before deployment, offering an objective assessment of platform security and reinforcing user confidence in how DeFi lending works.
Equally important is transparency across operations, governance, and risk management. Open-source code, publicly auditable smart contracts, and transparent governance help foster accountability. Regular audits and a strong commitment to transparency are crucial for maintaining a secure, reliable DeFi environment and strengthening confidence in the broader ecosystem.
Popular DeFi Lending Platforms
The DeFi lending landscape is characterized by a diverse array of platforms, each featuring unique functionalities and mechanisms. Exploring some of the most prominent and widely utilized platforms, such as Aave, Compound, and MakerDAO, provides valuable insights into the practical implementation of advanced DeFi loan management mechanisms and the diverse approaches to how DeFi lending works in practice.
Overview of Leading Platforms
Aave, Compound, and MakerDAO are consistently ranked among the most prominent and extensively utilized DeFi lending platforms in the market. Each platform has made substantial contributions to the growth and ongoing evolution of DeFi lending, showcasing distinct approaches to loan management and platform design within their respective DeFi loan management mechanisms and demonstrating the multifaceted nature of how DeFi lending works.
Aave is particularly recognized for its extensive range of supported assets, innovative features such as flash loans, and a strong emphasis on user experience optimization. Compound is widely acknowledged for its sophisticated algorithmic interest rate model and its strategic focus on facilitating institutional adoption. MakerDAO is renowned for its pioneering DAI stablecoin and its unique approach to lending and borrowing, utilizing DAI as both a loan and collateral asset within its ecosystem. These platforms, while sharing fundamental principles of robust DeFi loan management mechanisms, also exhibit distinct characteristics and cater to different user needs and preferences, collectively illustrating the versatility and adaptability of how DeFi lending works in diverse contexts.
Unique Platform Features
Each major DeFi lending platform offers unique features that set it apart and showcase different approaches to DeFi loan management mechanisms. Aave provides both variable and stable interest rates, letting users align choices with their risk preferences, and it pioneered flash loans — uncollateralized loans repayable within a single transaction block, enabling advanced DeFi strategies.
Compound stands out for its algorithmic, real-time interest rate adjustments, creating an efficient, responsive market, and emphasizes decentralized governance, allowing COMP token holders to shape protocol updates. MakerDAO’s defining feature is its DAI stablecoin, pegged to the US dollar, acting as both a borrowing and lending asset and offering an innovative stablecoin-centered model for how DeFi lending works.
Future Trends in DeFi Loan Management
The future trajectory of DeFi loan management is replete with exciting possibilities and transformative potential. Ongoing innovations in core lending mechanisms, the strategic integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) technologies, and evolving regulatory landscapes are all poised to significantly shape the next chapter of sophisticated DeFi loan management mechanisms and further refine the intricacies of how DeFi lending works.
Innovations in Lending Mechanisms
The DeFi space thrives on constant innovation, and DeFi loan management mechanisms are no exception. We can expect ongoing experimentation with new collateral types like real-world assets (RWAs) and NFTs, expanding how DeFi lending works with more diverse assets. Under-collateralized and uncollateralized models are also being explored, using advanced reputation systems or decentralized credit scoring to address the capital inefficiency of traditional over-collateralization.
Cross-chain lending protocols are emerging, enabling seamless borrowing and lending across multiple blockchains, further transforming how DeFi lending operates across ecosystems. Innovations in risk management — including adaptive liquidation methods and advanced insurance solutions — will be key to strengthening the security, stability, and long-term evolution of DeFi lending platforms, ensuring they work safely and reliably into the future.
AI & Machine Learning Integration
The strategic integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) holds immense potential to revolutionize sophisticated DeFi loan management mechanisms and greatly enhance the operational efficiency of how DeFi lending works. By analyzing vast datasets, AI and ML improve risk assessment, identifying patterns and predicting risks more accurately than traditional methods, thereby strengthening the robustness of DeFi systems.
AI-driven algorithms can also optimize interest rate models, adjusting them dynamically based on complex, real-time market factors for greater efficiency and responsiveness. Additionally, AI boosts fraud detection and improves the user experience by automating lending processes, streamlining how DeFi lending operates for users and platforms alike. Though still in its early stages, AI and ML’s ability to elevate efficiency, security, and risk management is undeniable and will play a major role in shaping the future of how DeFi lending evolves.
Regulatory Landscape Evolution
Regulation is a crucial and multifaceted force that will shape the future of DeFi loan management and significantly impact the global evolution of how DeFi lending works. Due to DeFi’s decentralized, borderless nature, regulators face complex challenges as they strive to balance oversight, consumer protection, and ongoing innovation in this rapidly changing space.
Achieving clear, well-defined regulations is essential for long-term DeFi growth, as it offers a stable framework for innovation, reduces uncertainty, and attracts institutional capital. While regulatory challenges persist, they also open the door for constructive dialogue and collaboration between regulators and the DeFi community, helping to build a balanced environment that supports both innovation and risk management — ultimately guiding the sustainable development of DeFi loan management mechanisms worldwide.
Expert Insights: Mastering DeFi Loan ManExpert Insights: Mastering DeFi Loan Management
Mastering effective loan management strategies is crucial for maximizing returns while minimizing risks as we navigate the dynamic landscape of decentralized finance (DeFi) lending. Here are key expert insights to help you optimize your DeFi lending experience:
- Diversify Your Collateral: Mitigate risk by utilizing a diverse portfolio of collateral assets.
- Monitor LTV Ratios: Vigilantly track your Loan-to-Value ratio, particularly during periods of market volatility. Implement LTV alerts for proactive risk management.
- Understand Interest Rates: Gain a comprehensive understanding of how interest rates are algorithmically set on your chosen platform. Factor in potential rate fluctuations for informed decision-making.
- Explore Rate Types: Strategically choose between fixed and variable interest rate options based on your individual risk tolerance and overarching financial objectives.
- Platform Governance: If you hold platform governance tokens, actively participate in DAO votes to influence platform evolution.
- Prioritize Security: Exclusively utilize reputable and thoroughly audited DeFi platforms. Develop a deep understanding of implemented security measures and acknowledge inherent risks. Consider utilizing insurance protocols for enhanced asset protection.
- Start Small: For newcomers to DeFi lending, commence with smaller capital allocations and progressively increase participation as you gain practical experience and in-depth understanding.
Tokenova: Secure Your DeFi Lending with Expert Compliance Solutions
Navigating DeFi loan management can be complex—smart contracts, collateralization, and liquidation risks demand expert oversight. Tokenova is your trusted partner in ensuring secure, compliant, and optimized DeFi lending strategies.
How Tokenova Helps You Master DeFi Lending
✔ Smart Contract Audits – Protect against vulnerabilities and ensure seamless automation.
✔ Regulatory Compliance – Stay ahead of evolving regulations across global jurisdictions.
✔ Risk Management Strategies – Minimize liquidation risks and optimize collateral efficiency.
✔ Custom DeFi Advisory – Get tailored solutions for DeFi lending platforms and yield generation.
Conclusion: Decentralized Lending’s Ascent
In conclusion, sophisticated DeFi loan management mechanisms are fundamentally revolutionizing the financial landscape by offering transparent, operationally efficient, and broadly accessible lending and borrowing solutions. The ingenious synergy of smart contracts, over-collateralization protocols, and algorithmic interest rate models forms the robust foundation of these innovative platforms, ensuring enhanced security and inherent stability within a decentralized environment and fundamentally transforming how DeFi lending works. While inherent risks remain, ongoing innovations in core technology, advanced risk management methodologies, and decentralized governance frameworks are continuously strengthening the overall DeFi lending ecosystem. As the DeFi sector matures and regulatory frameworks evolve to provide greater clarity, we anticipate even wider adoption and deeper integration of these groundbreaking DeFi loan management mechanisms into the global financial system. The future of lending is unequivocally becoming increasingly decentralized, and developing a comprehensive understanding of these core mechanisms is absolutely key for effectively participating in this transformative financial revolution and fully grasping the disruptive potential of how DeFi lending works.
Key Takeaways: DeFi Loan Management Essentials
- Smart Contracts & Over-collateralization: Foundational mechanisms ensuring loan security and process automation.
- LTV Ratios: Critically important for effective risk management and determining borrowing capacity.
- Automated Liquidation: Essential platform solvency mechanism, but presents inherent risks for borrowers.
- Algorithmic Interest Rates: Dynamic interest rates driven by real-time supply and demand dynamics.
- Decentralized Governance (DAOs): Community-led platform evolution and parameter adjustments.
- Security & Audits: Vital for building user trust and effectively mitigating inherent platform risks.
References: Springer, ResearchGate, Stanford JBLP, Wharton
What if the borrowed asset’s value skyrockets?
If the borrowed asset’s value increases significantly, it does not directly impact your deposited collateral. Your collateralization is primarily determined by the value of the collateral asset you provided and the Loan-to-Value (LTV) ratio established at the time of borrowing. However, if the value of your collateral asset also appreciates concurrently, your loan becomes even more over-collateralized, further reducing your overall liquidation risk profile. You retain the option to withdraw a portion of your collateral if the prevailing LTV ratio permits, but fluctuations in the price of the borrowed asset itself do not directly trigger any modifications to your collateral requirements.
Are DeFi loans reported to credit bureaus?
Currently, DeFi loans are generally not reported to traditional credit reporting agencies or bureaus. DeFi operates outside the purview of the conventional financial system, and standardized reporting mechanisms are not yet comprehensively integrated. Consequently, your DeFi-related borrowing and lending activities typically do not directly influence your traditional credit score. However, it is important to note that this landscape is subject to ongoing evolution, and as DeFi gains broader mainstream acceptance and regulatory frameworks mature, there may be future integrations or regulatory changes that could potentially lead to some form of reporting or interaction with established traditional credit systems. For the present time, DeFi lending operates largely autonomously and independently of traditional credit reporting infrastructures.
Can I lose more than my collateral in DeFi lending?
The over-collateralization mechanism inherent in DeFi lending protocols is specifically designed to prevent borrowers from incurring losses exceeding their initial collateral deposit. The automated liquidation process is intentionally implemented to sell off a portion of your deposited collateral to comprehensively cover the outstanding loan amount and any accrued interest. However, it is crucial to acknowledge that in highly improbable and extreme scenarios characterized by rapid and severe market downturns, or in the event of unforeseen and critical smart contract vulnerabilities being exploited, it is theoretically possible to experience losses that could potentially approach or, in truly exceptional black swan events coupled with sophisticated protocol exploits, even marginally exceed your initial collateral deposit. While robust DeFi platforms are meticulously engineered to mitigate these types of systemic risks, it remains imperative to understand that inherent risks still persist within the decentralized finance ecosystem, and prudent risk management practices, such as strategically diversifying collateral holdings and diligently monitoring LTV ratios, are absolutely essential for responsible participation.












