Navigating the world of blockchain and smart contracts can feel like charting unknown waters. You’re likely asking: what is the best blockchain for smart contracts? The answer, in short, isn’t one-size-fits-all. This comprehensive guide will illuminate the top contenders in the realm of top blockchain smart contracts and top smart contract platforms, providing you with the insights needed to make an informed decision. In this Article of Tokenova, We’ll explore the strengths and weaknesses of each platform, empowering you to select the ideal foundation for your next groundbreaking project.
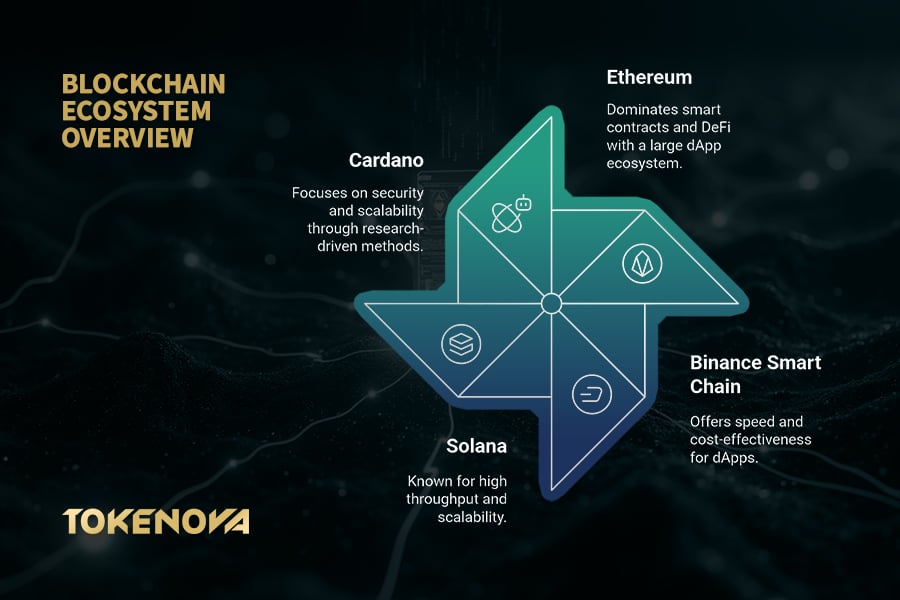
Ethereum: The Pioneering Powerhouse
Ethereum remains the cornerstone of the smart contract revolution, having introduced robust smart contract functionality in 2015. As of 2025, Ethereum boasts over 21,358 decentralized applications (dApps) across its ecosystem, supported by a developer community of more than 250,000 active contributors (antiersolutions), making it the most vibrant and mature blockchain ecosystem globally.
The platform continues to dominate the decentralized finance (DeFi) space, hosting 70% of all DeFi protocols and managing over $121.26 billion in total value locked (TVL), with leading protocols like Uniswap and Aave maintaining their market dominance. In 2022, Ethereum completed its transition to a proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus mechanism through “The Merge,” reducing its energy consumption by 99.95% and addressing long-standing environmental concerns. Post-Merge, Ethereum’s staking rewards have stabilized at 3.83% annually (chainlabo), attracting over 27.8 million ETH staked, which enhances network security and economic sustainability.
The Genesis of Smart Contracts on Ethereum
Before Ethereum, blockchains primarily facilitated cryptocurrency transactions. Vitalik Buterin’s vision for Ethereum expanded this by introducing the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). The EVM enables developers to execute arbitrary code, creating self-executing contracts with predefined rules.
This innovation opened up vast possibilities, from decentralized exchanges to intricate supply chain systems. The early success of projects like MakerDAO underscored the power of Ethereum’s smart contract capabilities, drawing numerous developers and entrepreneurs to the platform. Ethereum’s foundational role in pioneering programmable blockchains solidifies its position as a contender for the Best Blockchain for Smart Contracts.
Binance Smart Chain (BSC): Speed and Affordability Converge
When considering the Best Blockchain for Smart Contracts, Binance Smart Chain (BSC) emerged as a strong contender. Designed to run alongside Binance Chain, BSC offered a compelling alternative to Ethereum, especially during times of high network congestion, by providing significantly faster transaction times and lower fees. Imagine quick payments or trades with costs as low as a fraction of a cent and block confirmations in just 3 seconds. A major draw of BSC is its Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) compatibility, enabling developers to easily port their existing Ethereum projects with minimal changes, leveraging their current tools and expertise.
This interoperability has fueled rapid growth within the BSC ecosystem, attracting a diverse range of projects and users seeking efficient and cost-effective smart contract execution. For example, PancakeSwap, a decentralized exchange on BSC, quickly gained popularity due to its lower fees and faster transaction speeds compared to some of its Ethereum-based counterparts.
PancakeSwap’s thriving ecosystem, fueled by CAKE, demonstrates BSC’s practical benefits, attracting a significant user base. BSC’s Proof of Staked Authority (PoSA) consensus ensures high throughput and scalability, making it a preferred choice for DeFi. Its cross-chain interoperability further enhances its appeal, enabling seamless asset transfers and fostering a connected ecosystem.
BSC’s Rise and Ecosystem Growth
BSC’s rapid growth stems from more than just low fees. Binance’s active support, providing funding and resources to projects, was key. The EVM compatibility also enabled easy developer transition from Ethereum. This fostered a thriving ecosystem of DeFi and NFTs on BSC. Despite centralization critiques, BSC secured a significant niche by offering speed and affordability in the smart contract space.
Solana: The Need for Speed and Scale
For applications demanding lightning-fast transaction speeds and unparalleled scalability, Solana emerges as a frontrunner. This high-performance blockchain was architected from the ground up to handle a massive volume of transactions without compromising speed or security. With a throughput of up to 65,000 transactions per second (TPS) and transaction fees often under $0.01, Solana is a game-changer for industries requiring high-frequency operations, such as decentralized social media platforms, high-frequency trading systems, and real-time gaming applications.
Solana’s innovative consensus mechanisms, particularly its Proof of History (PoH), and unique architectural choices enable it to achieve throughput levels that were once considered unattainable. PoH acts as a cryptographic clock, creating a verifiable timeline for transactions, which significantly reduces the time needed for consensus. This, combined with its Proof of Stake (PoS) mechanism, ensures both speed and security, making Solana a robust platform for decentralized applications (dApps).
Solana stands out as a top contender for Best Blockchain for Smart Contracts, enabling complex dApps with near-instant finality and minimal costs. Its performance attracts innovation, exemplified by Serum, a decentralized exchange offering centralized-exchange-like speeds and features like limit orders.
Beyond Serum, Solana’s ecosystem thrives with Raydium, an AMM for efficient token swaps and yield farming, and its growing popularity for NFT marketplaces and gaming applications due to high transaction volumes and low latency.
Significant institutional adoption by entities like Franklin Templeton and Société Générale for asset tokenization and real-time payments further cements Solana’s leadership. Its expanding ecosystem, institutional support, and tech innovations position Solana as a dominant force in blockchain beyond 2025.
Solana’s Technological Innovations
Solana’s remarkable performance stems from key tech innovations. Proof of History (PoH), acting as a decentralized clock, enables quick transaction ordering by reducing constant node communication. Further boosts come from Turbine (block propagation) and Gulf Stream (transaction forwarding).
Though these offer major advantages, they also bring complexities developers must weigh. Solana’s swift growth and adoption confirm its leading spot for applications demanding extreme scalability.
Cardano: A Research-Driven Approach to Security and Scalability
Cardano stands out with its rigorous, research-driven and peer-reviewed blockchain development, prioritizing security, scalability, and long-term sustainability. Its layered architecture separates the settlement and computational layers for enhanced flexibility and upgrades. Cardano’s dedication to formal verification for smart contracts ensures intended code behavior and reduces vulnerabilities, making it a robust and reliable platform for critical applications.
For instance, projects focused on identity management (e.g., Atala PRISM) or supply chain traceability (e.g., Beefchain), where security and reliability are paramount, might find Cardano’s approach particularly appealing. The focus on formal verification aims to minimize the risk of costly errors and exploits, making it a preferred choice for industries requiring high levels of trust and transparency.
Additionally, Cardano’s Ouroboros consensus mechanism, a proof-of-stake protocol, is designed to be energy-efficient and scalable, addressing common issues faced by earlier blockchain networks. This, combined with its research-driven development and community-centric governance model, ensures that Cardano remains at the forefront of blockchain innovation. Projects like Hydra, a layer-2 scaling solution, further enhance Cardano’s capabilities, enabling it to handle thousands of transactions per second while maintaining security and decentralization.
Read More: Layer 2 Solutions: Boosting Blockchain Scalability
In summary, Cardano’s scientific philosophy, layered architecture, and commitment to formal verification make it a unique and reliable platform for a wide range of applications, from decentralized finance (DeFi) to real-world asset tokenization and beyond.
Cardano’s Emphasis on Formal Verification
Cardano sets itself apart with formal verification, using mathematical proofs to ensure smart contract code correctness. This rigorous process drastically reduces bugs and vulnerabilities, offering superior assurance over traditional testing. This commitment reflects Cardano’s focus on a secure, reliable foundation for dApps. Its smart contract platform, Plutus, is heavily influenced by formal methods, empowering developers to create demonstrably correct code.
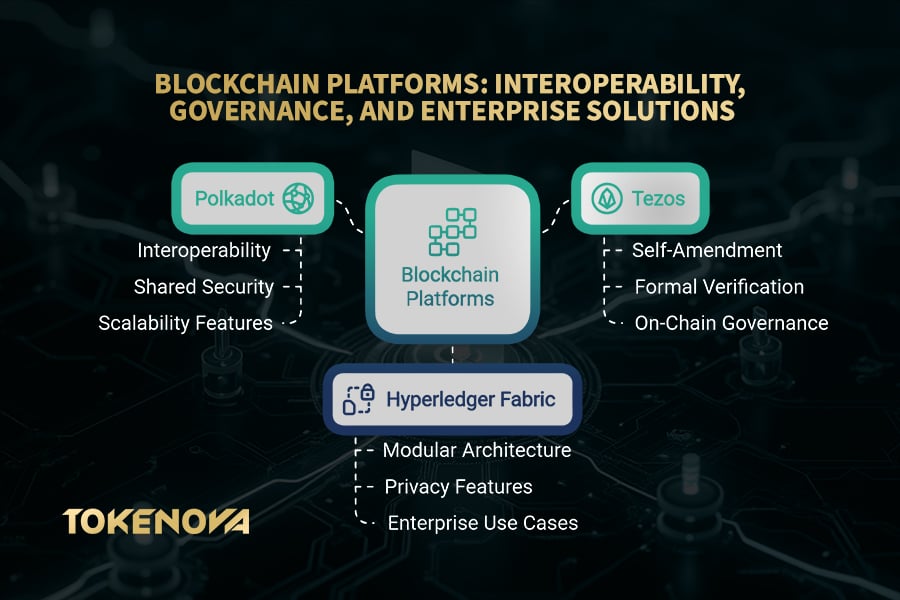
Polkadot: The Internet of Blockchains
Imagine a world where different blockchains can seamlessly communicate and share information. This is the vision of Polkadot, a next-generation multi-chain framework designed to foster interoperability between disparate blockchain networks. Think of it as a central hub connecting various specialized blockchains, allowing them to work together in a unified ecosystem. Polkadot’s unique architecture enables different blockchains, known as parachains, to connect to a central relay chain, benefiting from shared security and the ability to exchange data and assets through its native Cross-Consensus Messaging Format (XCM).
Polkadot creates an interconnected ecosystem for cross-chain applications, enabling seamless interaction between specialized blockchains called parachains. Its architecture, emphasizing features like multi-core and elastic scaling, makes it a powerful platform for complex, decentralized systems.
Projects like Acala highlight this interoperability with DeFi services spanning parachains. With its 2025 roadmap, including XCM v5 and DOT as a universal gas token, Polkadot aims to strengthen its leadership in blockchain connectivity, cementing its position as a Best Blockchain for Smart Contracts.
Polkadot’s Interoperability and Shared Security
Polkadot revolutionizes the blockchain landscape by connecting diverse blockchains through its central relay chain. This architecture offers shared security to connected parachains, eliminating their need for independent security setups and simplifying new blockchain launches. Crucially, Polkadot’s cross-chain messaging protocol (XCMP) allows seamless communication and data transfer between parachains, fostering a highly interoperable multi-chain ecosystem for various applications.
Tezos: The Self-Improving Blockchain
Tezos differentiates itself as a self-amending blockchain, capable of evolving its protocol without hard forks. This unique on-chain governance mechanism allows seamless updates, ensuring long-term adaptability, as demonstrated by 14 successful protocol upgrades. In a separate but related advancement for multi-chain ecosystems, Polkadot’s Cross-Chain Messaging Protocol (XCMP) facilitates communication and data transfer between parachains, positioning it for future interoperability.
Furthermore, Tezos emphasizes formal verification for smart contracts, providing developers with tools to mathematically prove the correctness of their code, significantly reducing the risk of errors and vulnerabilities. The Michelson language, Tezos’ native smart contract language, is designed with formal verification in mind, enabling developers to ensure their contracts are secure and reliable. This focus on security has made Tezos a preferred platform for industries requiring high levels of precision, such as finance and supply chain management.
Tezos’ on-chain governance lets stakeholders (bakers) propose, vote on, and implement protocol upgrades through a five-period process (Proposal, Exploration, Cooldown, Promotion, Adoption). This community-driven approach ensures beneficial evolution, as seen with successful upgrades like Nairobi and Oxford.
The blend of self-amendment, formal verification, and on-chain governance enables seamless upgrades, avoiding disruptive hard forks common on other blockchains. For example, Smart Rollups in 2023 boosted Tezos to 1 million transactions per second, highlighting its scalability and adaptability. The Tezos X roadmap will further enhance performance, composability, and interoperability, reinforcing Tezos’ leadership as a Best Blockchain for Smart Contracts.
Tezos’ On-Chain Governance and Formal Verification
Tezos’ on-chain governance system allows token holders to propose, vote on, and implement changes to the protocol. This decentralized decision-making process ensures that the blockchain can adapt and evolve over time without requiring contentious hard forks that can split the community. The emphasis on formal verification, similar to Cardano, provides developers with tools to mathematically prove the correctness of their smart contracts, enhancing security and reliability. These features contribute to Tezos’ reputation as a robust and future-proof platform for building decentralized applications.
Hyperledger Fabric: Enterprise-Grade Permissioned Solutions
Hyperledger Fabric offers a distinct, permissioned blockchain approach, prioritizing privacy, control, and scalability for enterprise solutions. Unlike public chains, it’s a private network, limiting access to authorized users.
Its modular architecture allows customization of components like consensus mechanisms and membership services. This flexibility, plus its emphasis on privacy and security, makes it ideal for supply chain management, financial services, and healthcare. For instance, in supply chains, only authorized partners can access and update data, ensuring integrity and transparency and establishing a single source of truth, as demonstrated by Walmart.
In financial services, Hyperledger Fabric is being used to streamline processes like cross-border payments and asset tokenization. For instance, a corporate remittance network built on Hyperledger Fabric allows banks to share real-time compliance and anti-money laundering (AML) data, reducing the time and cost associated with traditional payment methods. Additionally, asset tokenization where physical or digital assets are represented as digital tokens on the blockchain has opened up new opportunities for fractional ownership and liquidity, particularly in industries like real estate and art.
Hyperledger Fabric excels in enterprise blockchain with privacy features like channels for isolated networks and private data collections for confidential sharing. Its permissioned model, modular architecture, and privacy-focused design make it ideal for secure, transparent, and efficient applications in supply chain management, financial services, and asset tokenization. Fabric is set to shape enterprise blockchain’s future as businesses embrace these solutions.
Hyperledger Fabric’s Modular Architecture and Use Cases
Hyperledger Fabric’s modular design lets enterprises customize its blockchain for specific needs, offering choices in consensus, membership, and storage. This flexibility suits diverse uses like supply chain tracking, asset management, and identity verification. Its permissioned network ensures only authorized access, boosting privacy and control. Hosted by the Linux Foundation, it promotes open-source collaboration in enterprise blockchain.
Decoding the Best Fit: A Smart Contract Platform Showdown
Choosing the best blockchain for smart contracts requires a careful evaluation of several critical factors. Let’s delve into a comparative analysis across key dimensions:
Security: Fortifying Your Smart Contracts
Security in smart contracts is crucial. Ethereum, despite being battle-tested, saw the 2016 DAO hack due to vulnerabilities, stressing rigorous auditing. Cardano and Tezos prioritize security via research-driven development and formal verification. Permissioned chains like Hyperledger Fabric offer inherent security through controlled access. Solana, despite speed, has faced stability issues. BSC shares Ethereum’s security concerns. Polkadot’s shared security model bolsters its parachains.
Scalability: Handling the Transaction Load
Scalability is key for blockchains handling transactions. Solana boasts high throughput (thousands/second). Polkadot scales via parachains distributing loads. BSC offers faster transactions than Ethereum, but can face congestion.
Ethereum’s upgrades (sharding) target scalability. Cardano’s layered design prioritizes it despite current lower throughput. Tezos focuses on stability. Hyperledger Fabric’s scalability is configurable for enterprise needs.
Read More: Blockchain Scalability Challenges: Top Solutions for 2025
Development Environment: Empowering Builders
A vibrant development environment is key. Ethereum leads with its vast, mature ecosystem, tools (Truffle, Remix), and large community. BSC, being EVM-compatible, shares many of these benefits.
Solana’s Rust-based environment is expanding rapidly. Cardano emphasizes secure development with Plutus and Marlowe. Polkadot provides unique Substrate tools for parachains. Tezos offers strong formal verification tools, supporting Michelson. Hyperledger Fabric delivers a modular, customizable enterprise environment, supporting Go and Java.
Transaction Costs: The Price of Execution
Transaction costs (gas fees) vary greatly. Solana boasts incredibly low fees (fractions of a cent). BSC offers lower fees than Ethereum. Ethereum fees fluctuate, becoming very high during congestion (e.g., 2021 NFT craze).
Cardano targets predictable costs. Polkadot fees depend on the parachain. Tezos generally has low fees. Hyperledger Fabric’s internal costs aren’t directly comparable to public blockchains.
Ecosystem and Adoption: Real-World Impact
A platform’s ecosystem maturity and adoption signal its potential. Ethereum leads in dApps (Uniswap, Aave) and DeFi. BSC rapidly grew in DeFi (PancakeSwap). Solana’s NFT/DeFi ecosystem expands (Magic Eden). Cardano focuses on R&D, with supply chain and identity projects. Polkadot’s parachains enhance interoperability. Tezos sees adoption in digital collectibles (Hic et Nunc). Hyperledger Fabric is widely adopted by enterprises (Walmart supply chain, trade finance).
Choosing the best blockchain for smart contracts requires a careful evaluation of several critical factors. Let’s delve into a comparative analysis across key dimensions:
| Platform | Security | Scalability | Development Environment | Transaction Costs | Ecosystem and Adoption |
| Ethereum | High security but has faced vulnerabilities (e.g., DAO hack). Rigorous auditing is essential. | Moderate scalability; Layer 2 solutions and Ethereum 2.0 upgrades aim to improve. | Largest ecosystem with tools like Truffle and Remix. Extensive developer community. | High gas fees during congestion; can be costly for frequent transactions. | Largest and most diverse ecosystem with dApps like Uniswap and Aave. |
| Binance Smart Chain (BSC) | EVM-compatible; inherits Ethereum’s security considerations. Fewer validators raise centralization concerns. | Faster than Ethereum but can experience congestion during peak periods. | EVM-compatible; easy transition for Ethereum developers. Growing toolset. | Lower fees than Ethereum; affordable for frequent transactions. | Rapid growth in DeFi; platforms like PancakeSwap gaining traction. |
| Solana | High security but has faced network outages and stability issues. | Extremely high throughput (65,000 TPS); ideal for high-frequency applications. | Rapidly growing support for Rust and C. Increasing developer resources. | Very low fees (fractions of a cent); cost-effective for high-volume transactions. | Expanding ecosystem in NFTs and DeFi; projects like Magic Eden. |
| Cardano | Research-driven; formal verification ensures high security. | Layered architecture designed for scalability; currently lower throughput. | Evolving tools with a focus on security. Uses Haskell for smart contracts. | Predictable and reasonable fees; cost-effective for most use cases. | Growing ecosystem with a focus on real-world applications like supply chain and identity. |
| Polkadot | Shared security model for parachains; robust foundation. | Multi-chain architecture distributes transaction load; high scalability potential. | Unique development experience with Substrate framework. Supports Rust and Solidity. | Variable fees depending on the parachain; generally moderate. | Evolving ecosystem with a focus on interoperability and cross-chain functionality. |
| Tezos | Formal verification ensures high security; self-amending blockchain. | Stable and reliable; not focused on extreme throughput. | Robust tools for formal verification. Supports Michelson for smart contracts. | Low fees; affordable for most use cases. | Adoption in digital collectibles and security tokens; platforms like Hic et Nunc. |
| Hyperledger Fabric | Permissioned blockchain; high security due to controlled access. | Scalability tailored to enterprise needs; highly customizable. | Modular and customizable; supports Go and Java. Ideal for enterprise solutions. | Internal costs managed within the enterprise network; not directly comparable. | Widely adopted in enterprise settings (e.g., Walmart for supply chain management). |
This comparison highlights the strengths and weaknesses of each platform, helping you identify the best blockchain for smart contracts based on your project’s unique needs. Whether you prioritize security, scalability, or cost-effectiveness, there’s a platform tailored to your requirements.
Strategic Selection: Tailoring Your Blockchain Choice
The quest for the best blockchain for smart contracts ultimately boils down to aligning platform capabilities with your specific project needs. Let’s explore key considerations:
Use Case Requirements: Matching Needs to Capabilities
Carefully analyze the specific requirements of your project. Do you need ultra-high transaction speeds, like for a decentralized gaming platform with millions of users? Is security your absolute top priority, such as for a system managing sensitive financial data? Are low transaction costs essential for a micro-payment application? Does your application require interoperability with other blockchains to access specific data or functionalities? Understanding your core needs will significantly narrow down your options. For instance, a high-frequency trading platform might lean towards Solana, while a supply chain management solution might find Hyperledger Fabric more suitable.
A decentralized finance (DeFi) application might consider the established ecosystem of Ethereum or the lower fees of BSC. Consider the example of a decentralized identity solution. If regulatory compliance and data privacy are paramount, a permissioned blockchain like Hyperledger Fabric might be the ideal choice. Conversely, if the goal is to create a globally accessible and censorship-resistant identity system, a public blockchain like Ethereum or Cardano might be more appropriate.
Read More: Best Blockchain for Tokenization: Your Ultimate Guide
Community and Support: The Power of Collaboration
A vibrant and supportive developer community is invaluable. A strong community provides readily available resources, helps troubleshoot issues, and fosters innovation. Ethereum boasts the largest and most active community, with countless online forums, developer groups, and open-source projects. BSC benefits from its close ties to the Binance ecosystem, providing access to a large user base and developer network. Solana’s community is rapidly growing, with increasing resources and support available through its developer documentation and online communities.
Cardano has a dedicated and research-focused community, often engaging in in-depth technical discussions. Polkadot’s community is focused on building and connecting parachains, with a strong emphasis on collaboration and interoperability. Tezos has a strong community focused on governance and formal verification, actively participating in protocol upgrades. Hyperledger Fabric has a strong enterprise-focused community, with support provided by the Linux Foundation and various enterprise partners.
Regulatory Compliance: Navigating the Legal Landscape
In an evolving regulatory landscape, considering compliance aspects is crucial. Different jurisdictions have varying regulations regarding blockchain technology and smart contracts. Permissioned blockchains like Hyperledger Fabric offer greater control and transparency, which can be advantageous for compliance, as organizations can control who participates in the network and what data is shared.
Public blockchains are working towards solutions that address regulatory concerns, such as zero-knowledge proofs and privacy-preserving technologies. For example, when considering a blockchain for issuing security tokens, understanding the specific regulations in the target jurisdictions is paramount. Some regulations may require specific identity verification processes or restrictions on who can participate, making a permissioned blockchain a more suitable choice. Understanding the legal and regulatory implications in your target markets is essential when choosing a platform.
Future Development and Roadmap: Looking Ahead
Evaluate the long-term vision and development roadmap of each platform. Are there upcoming upgrades or features that align with your project’s future needs? A platform with a clear and ambitious roadmap indicates its commitment to innovation and long-term sustainability. Staying informed about the future direction of each blockchain will help you make a future-proof decision.
For instance, Ethereum’s ongoing development towards “Ethereum 2.0” with sharding and further improvements to its consensus mechanism is a significant factor for projects planning long-term on the platform. Similarly, understanding Cardano’s roadmap for further scalability and governance enhancements is crucial for projects considering building on it.
Pro Strategies for Smart Contract Deployment
Successfully deploying smart contracts involves more than just choosing the right blockchain. Here are some crucial strategies to consider:
- Rigorous Auditing: Before deploying any smart contract to a live network, ensure it undergoes thorough security audits by reputable third-party firms. This helps identify and mitigate potential vulnerabilities before they can be exploited. Companies like Trail of Bits and ConsenSys Diligence are well-known for their expertise in smart contract auditing. For example, in 2023, ConsenSys Diligence identified a critical vulnerability in a DeFi protocol that could have led to the loss of millions of dollars, showcasing the importance of professional audits.
- Thorough Testing: Implement comprehensive testing procedures, including unit tests, integration tests, and simulated mainnet deployments on test networks, to ensure your smart contracts function as intended under various conditions. Tools like Ganache and Hardhat are commonly used for testing smart contracts in a local environment. For instance, Hardhat’s advanced debugging features allow developers to simulate complex scenarios, such as high network congestion, to test contract resilience.
- Gas Optimization: Write efficient smart contract code to minimize gas consumption, especially on networks with higher transaction fees. Techniques like optimizing data storage, using efficient data structures, and reducing unnecessary computations can significantly lower costs. For example, the Ethereum Gas Optimization Guide provides detailed strategies for reducing gas usage, such as using uint256 instead of smaller data types where possible.
- Upgradeability Considerations: Plan for potential future upgrades to your smart contracts. Implement upgrade patterns that allow you to modify your contracts without requiring a complete redeployment, which can be complex and costly. Proxy patterns, such as the Transparent Proxy or UUPS Proxy, are common approaches to achieve smart contract upgradeability. The OpenZeppelin Upgrades Plugin is a widely used tool for managing upgradeable contracts securely.
- Security Best Practices: Adhere to established security best practices for smart contract development, such as avoiding common vulnerabilities like reentrancy attacks and ensuring proper access controls. Resources like the Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP) provide valuable guidance on secure coding practices. For example, the Checks-Effects-Interactions pattern is a widely recommended practice to prevent reentrancy vulnerabilities.
- Community Engagement: Engage with the developer community for the chosen blockchain. Leverage their expertise, seek feedback, and stay updated on the latest best practices and potential security threats. Participating in online forums like Ethereum Stack Exchange or developer communities like Solidity Gitter can provide valuable insights and support. For instance, the Ethereum community regularly shares updates on emerging threats, such as front-running attacks, and discusses mitigation strategies.
Tokenova: Your Partner in Blockchain Innovation
At Tokenova, we understand the complexities of the blockchain landscape and the critical importance of choosing the right platform for your smart contract project. Our team of experienced blockchain developers and consultants provides end-to-end solutions, from initial concept and platform selection to smart contract development, auditing, and deployment.
We help businesses navigate the technical intricacies and make informed decisions that align with their specific goals and requirements. Whether you’re exploring the potential of DeFi on Ethereum, seeking high-throughput solutions on Solana, or require the security and control of Hyperledger Fabric, Tokenova is your trusted partner in blockchain innovation. We offer tailored services to help you unlock the transformative power of smart contracts and build the decentralized future.
Conclusion
The landscape of top blockchain smart contracts is dynamic and ever-evolving. There is no single “best” blockchain; the optimal choice hinges on the unique requirements of your project. Ethereum’s pioneering spirit and vast ecosystem remain compelling. BSC offers a cost-effective and efficient alternative. Solana shines with its unparalleled speed and scalability.
Cardano emphasizes security and a research-driven approach. Polkadot fosters interoperability and cross-chain innovation. Tezos offers self-amendment and robust security features. Hyperledger Fabric provides enterprise-grade permissioned solutions.
Ultimately, selecting the right platform requires careful consideration of factors like security, scalability, development environment, transaction costs, ecosystem maturity, and regulatory compliance. By thoroughly evaluating your needs and the strengths of each platform, you can confidently choose the best blockchain for smart contracts to bring your vision to life.
Key Takeaways
- Ethereum remains the leading platform with a vast ecosystem but can have higher gas fees.
- Binance Smart Chain offers lower fees and faster transactions, with EVM compatibility.
- Solana excels in speed and scalability, ideal for high-throughput applications.
- Cardano prioritizes security and a research-driven approach.
- Polkadot enables interoperability between different blockchains.
- Tezos offers self-amendment and strong security features.
- Hyperledger Fabric is ideal for enterprise solutions requiring permissioned access.
- Carefully consider your project’s specific needs when choosing a blockchain.
- Security audits and thorough testing are crucial for smart contract deployment.
References:
Top 9 smart contract platforms to consider in 2025
10 Best Smart Contract Platforms in 2024
An overview on smart contracts: Challenges, advances and platforms
How do gas fees impact the choice of blockchain for smart contracts?
Gas fees, the transaction costs on a blockchain, can significantly impact the overall cost of running a smart contract application. Blockchains with lower gas fees, like Solana or BSC, can be more attractive for applications with frequent transactions or a large user base. High gas fees on networks like Ethereum can make certain applications economically unviable. Therefore, understanding the typical gas fee structure of a blockchain is crucial for budget planning and application feasibility. For instance, if you’re building a micro-payment system where users make frequent small transactions, high gas fees would quickly erode the value of those transactions, making a low-fee blockchain a more sensible choice.
What role does the programming language play in selecting a smart contract platform?
The programming language supported by a blockchain platform directly impacts the developer experience and the availability of talent. Ethereum primarily uses Solidity, which has a large community and extensive resources, making it easier to find experienced developers. Other platforms may support different languages or variations. If your team has expertise in a particular language, choosing a platform that supports it can streamline development and reduce the learning curve. Furthermore, the maturity and security of the programming language itself are important considerations. A well-established language with robust tooling and security features can contribute to the overall reliability of your smart contracts.
Are there any emerging blockchain platforms for smart contracts worth considering?
While the established platforms dominate, several promising emerging blockchains are gaining traction in the smart contract space. These platforms often focus on addressing specific limitations of existing blockchains, such as scalability, interoperability, or energy efficiency. Staying informed about these newer platforms and their unique features can provide a competitive edge and potentially offer solutions tailored to niche requirements. However, it’s important to assess their maturity, security, and community support before committing to them for critical projects. Examples of emerging platforms include Avalanche (Avalanche), known for its high throughput and fast finality, and Flow (Flow), designed for NFTs and gaming. Evaluating their track record, developer activity, and security audits is crucial before adopting them.